“Residential solar wiring diagram”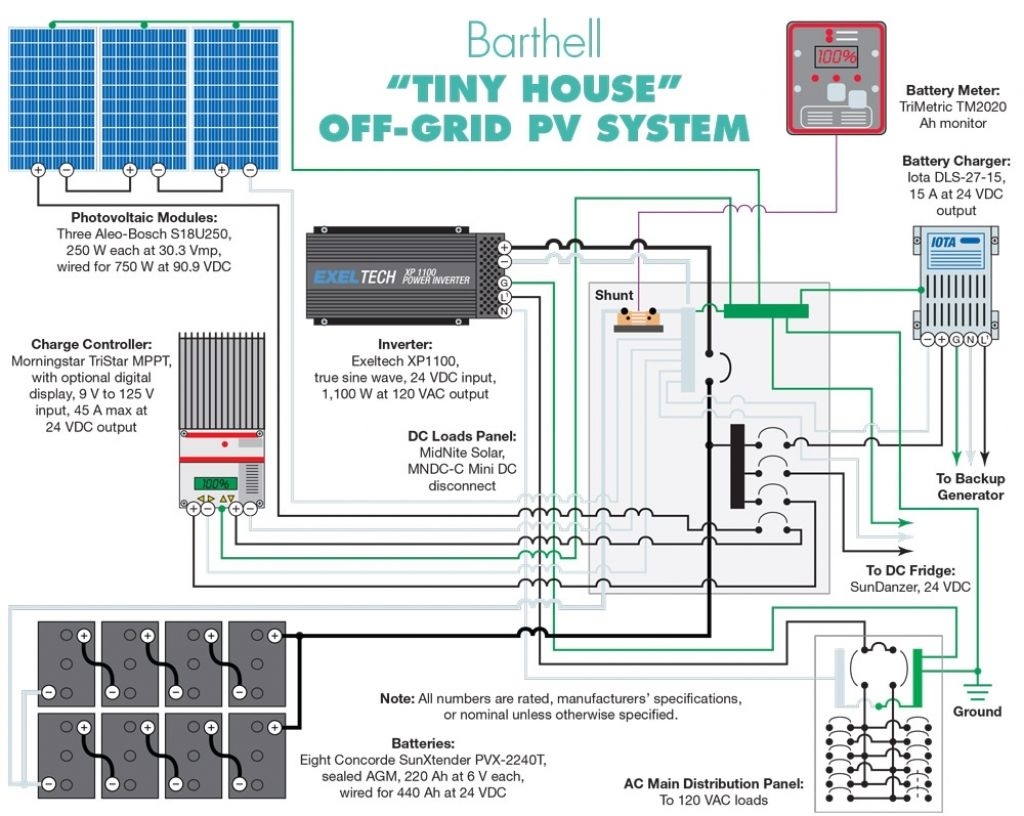
A well-designed solar wiring diagram is essential for a safe and efficient residential solar power system. In this article, we will delve into the world of residential solar wiring diagrams, exploring the key components, best practices, and regulations to ensure a successful installation.
Introduction to Residential Solar Power Systems
A residential solar power system is a complex network of components that work together to generate electricity from sunlight. The system typically consists of solar panels, a mounting system, a charge controller, a battery bank, an inverter, and a grid tie system. The solar panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then fed into the charge controller. The charge controller regulates the flow of energy to the battery bank, where excess energy is stored for later use. The inverter converts the DC electricity from the battery bank into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is then fed into the grid tie system and distributed throughout the home.
Components of a Residential Solar Wiring Diagram
A residential solar wiring diagram typically includes the following components:
- Solar Panels: The solar panels are the backbone of the system, converting sunlight into DC electricity. The panels are typically connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and current.
- Charge Controller: The charge controller regulates the flow of energy from the solar panels to the battery bank, preventing overcharging and ensuring the batteries are charged efficiently.
- Battery Bank: The battery bank stores excess energy generated by the solar panels for later use. The batteries are typically deep cycle batteries, designed to withstand repeated charge and discharge cycles.
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC electricity from the battery bank into AC electricity, which is then fed into the grid tie system.
- Grid Tie System: The grid tie system connects the solar power system to the utility grid, allowing excess energy to be sold back to the grid and ensuring a seamless transition between solar and grid power.
- Grounding System: The grounding system is essential for safety, providing a path to ground for fault currents and ensuring the system is properly bonded.
- Disconnects: Disconnects are used to isolate the system from the grid and allow for safe maintenance and repair.

Best Practices for Residential Solar Wiring Diagrams
To ensure a safe and efficient residential solar power system, the following best practices should be followed:
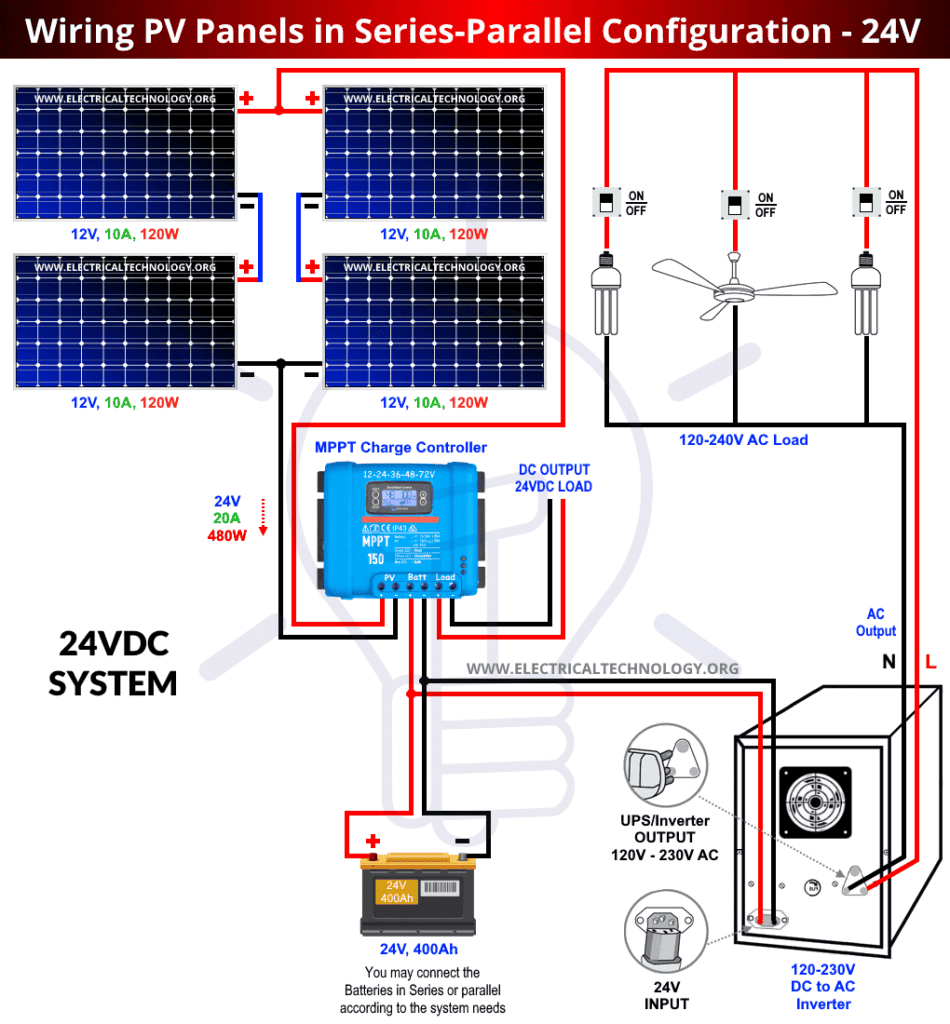
- Use a Standardized Wiring Diagram: A standardized wiring diagram ensures that the system is easy to understand and troubleshoot.
- Use Color-Coded Wiring: Color-coded wiring helps to identify the different components and connections, making it easier to troubleshoot and maintain the system.
- Use Proper Wire Sizing: Proper wire sizing ensures that the system can handle the maximum anticipated current, reducing the risk of overheating and electrical fires.
- Use Ground Fault Protection: Ground fault protection is essential for safety, providing protection against electrical shock and ensuring the system is properly grounded.
- Use Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Lockout/tagout procedures ensure that the system is safely isolated from the grid and other energy sources during maintenance and repair.

Regulations and Standards for Residential Solar Wiring Diagrams
The following regulations and standards apply to residential solar wiring diagrams:
- National Electric Code (NEC): The NEC provides guidelines for the safe installation of electrical systems, including solar power systems.
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): The IEC provides international standards for electrical systems, including solar power systems.
- Underwriters Laboratories (UL): UL provides certification and testing for electrical components, including solar panels, inverters, and charge controllers.
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): IEEE provides standards and guidelines for electrical systems, including solar power systems.
Designing a Residential Solar Wiring Diagram
To design a residential solar wiring diagram, the following steps should be followed:
- Determine the System Size: Determine the size of the system based on the energy requirements of the home and the available space for the solar panels.
- Choose the Components: Choose the components, including the solar panels, charge controller, battery bank, inverter, and grid tie system.
- Determine the Wiring Requirements: Determine the wiring requirements, including the wire size, type, and color.
- Create a Wiring Diagram: Create a wiring diagram, using a standardized format and including all the necessary components and connections.
- Review and Test the Diagram: Review and test the diagram to ensure it meets all the necessary regulations and standards.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Residential Solar Wiring Diagrams
The following common mistakes should be avoided in residential solar wiring diagrams:
- Incorrect Wire Sizing: Incorrect wire sizing can lead to overheating and electrical fires.
- Inadequate Grounding: Inadequate grounding can lead to electrical shock and safety hazards.
- Insufficient Disconnects: Insufficient disconnects can make it difficult to safely isolate the system from the grid and other energy sources.
- Incorrect Component Selection: Incorrect component selection can lead to inefficiencies and safety hazards.
- Inadequate Testing and Commissioning: Inadequate testing and commissioning can lead to safety hazards and system failures.
Conclusion
A well-designed residential solar wiring diagram is essential for a safe and efficient residential solar power system. By following best practices, regulations, and standards, and avoiding common mistakes, homeowners can ensure a successful installation that meets their energy needs and provides a safe and reliable source of renewable energy. Whether you’re a homeowner, installer, or designer, this comprehensive guide provides the necessary information to create a safe and efficient residential solar wiring diagram.
Recommendations for Future Improvements
As the solar industry continues to evolve, there are several recommendations for future improvements:
- Increased Standardization: Increased standardization of wiring diagrams and components can simplify the design and installation process.
- Advances in Technology: Advances in technology, such as smart inverters and energy storage systems, can improve the efficiency and reliability of residential solar power systems.
- Improved Safety Features: Improved safety features, such as arc fault protection and ground fault protection, can enhance the safety of residential solar power systems.
- Increased Education and Training: Increased education and training for installers and designers can ensure that residential solar power systems are designed and installed to meet the necessary regulations and standards.
- Greater Accessibility: Greater accessibility to residential solar power systems, including financing options and incentives, can make it easier for homeowners to adopt renewable energy sources.
By following the guidelines and recommendations outlined in this article, homeowners and installers can create a safe and efficient residential solar wiring diagram that meets their energy needs and provides a reliable source of renewable energy. As the solar industry continues to evolve, it’s essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments and advancements to ensure a successful installation that meets the necessary regulations and standards.


