“Home solar system circuit schematics”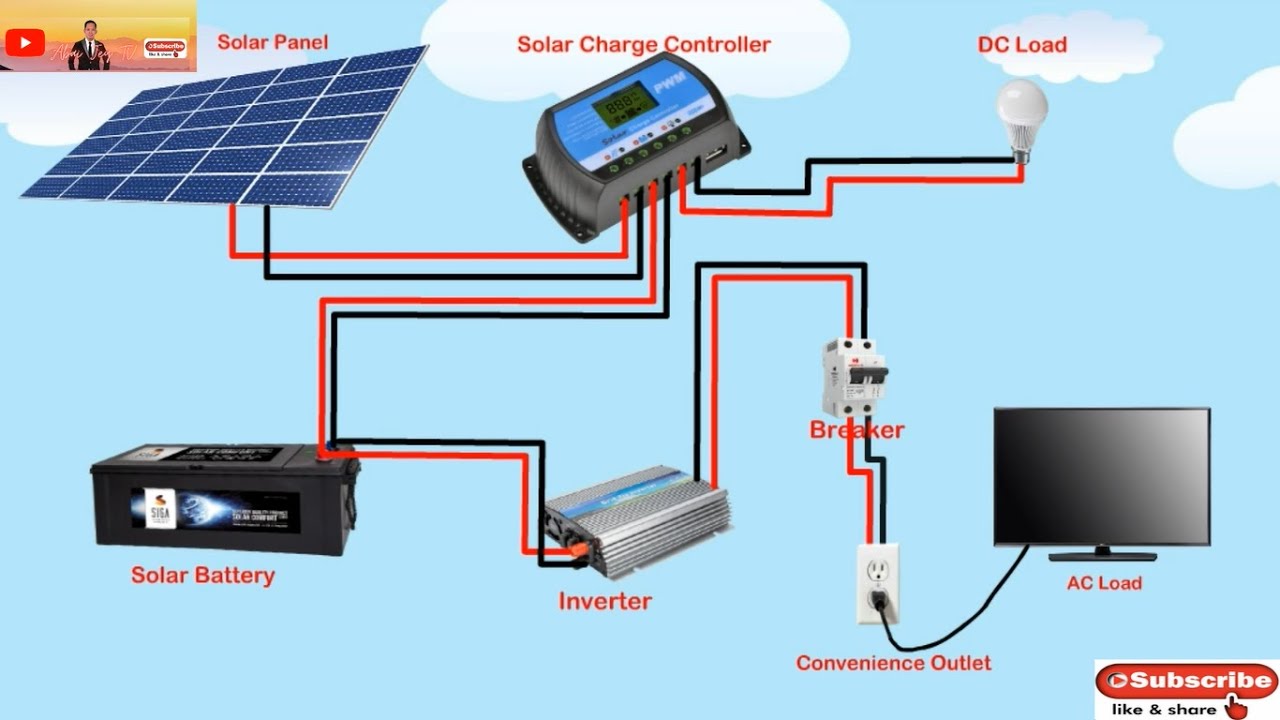
Solar panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
Design Considerations for Solar System Circuit Schematics
When designing a solar system circuit schematic, there are several key considerations to keep in mind:
- System Size and Configuration: The size and configuration of the system will determine the number of solar panels, batteries, and other components required.
- Energy Requirements: The energy requirements of the home or business will determine the size of the system and the amount of energy that needs to be stored in the batteries.
- Charge Controller Selection: The charge controller must be selected based on the size of the system and the type of batteries used.
- Inverter Selection: The inverter must be selected based on the size of the system and the type of loads that will be connected to the system.
- Safety Considerations: The system must be designed with safety in mind, including features such as overcurrent protection, ground fault protection, and arc fault protection.

Types of Solar System Circuit Schematics
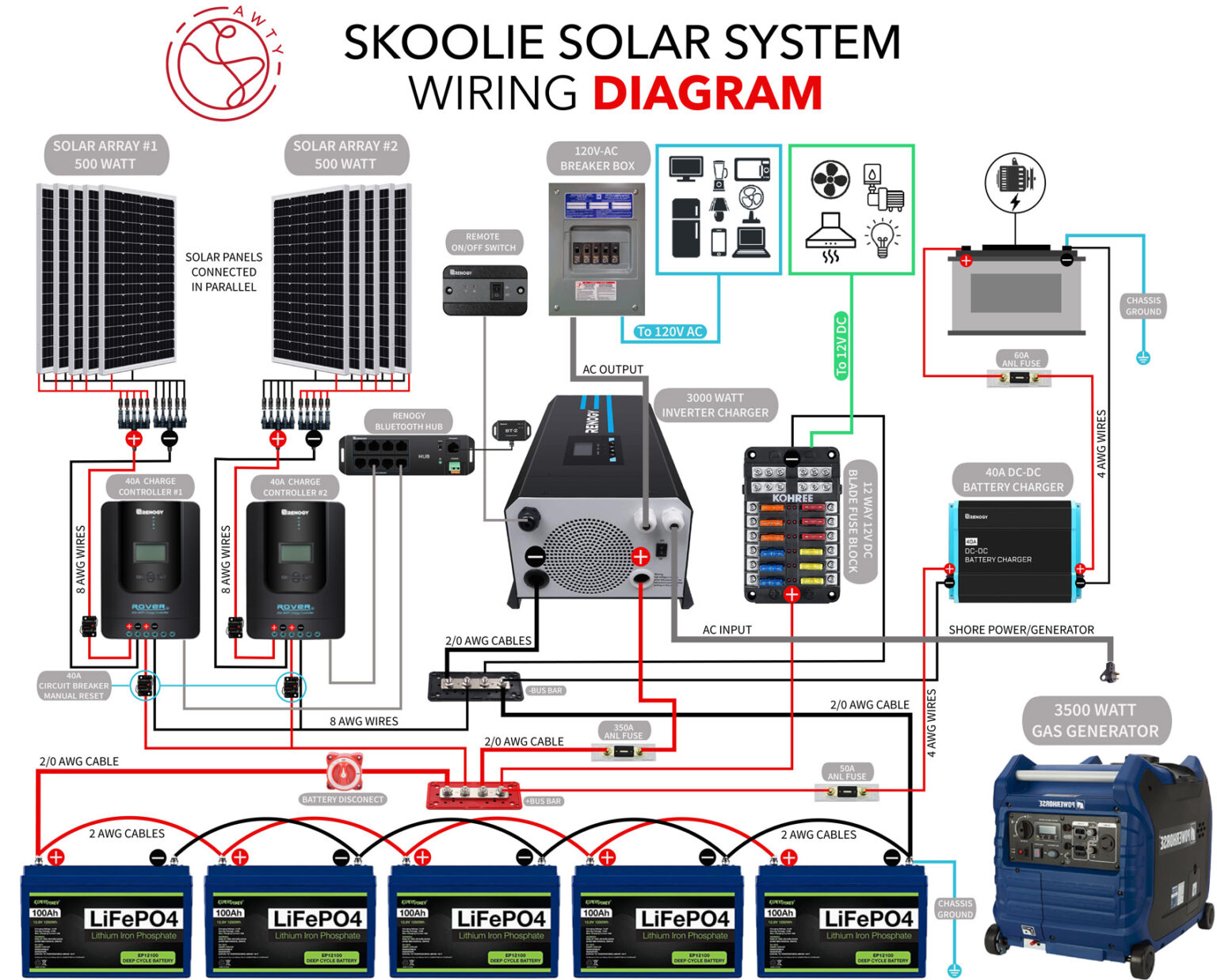
There are several types of solar system circuit schematics, including:
- Series Circuit Schematic: This type of schematic shows the components connected in series, with each component connected to the next in a single loop.
- Parallel Circuit Schematic: This type of schematic shows the components connected in parallel, with each component connected to the same two points.
- Combination Circuit Schematic: This type of schematic shows a combination of series and parallel connections.

Best Practices for Creating a Solar System Circuit Schematic
When creating a solar system circuit schematic, there are several best practices to follow:
- Use a Standardized Symbol Set: Use a standardized set of symbols to represent the various components in the system.
- Show All Connections: Show all connections between components, including wiring and connectors.
- Label All Components: Label all components, including solar panels, charge controllers, batteries, inverters, and electrical panels.
- Include Safety Features: Include safety features such as overcurrent protection, ground fault protection, and arc fault protection.
- Use a Scaling Factor: Use a scaling factor to ensure that the schematic is proportional to the actual system.
Software for Creating Solar System Circuit Schematics
There are several software programs available for creating solar system circuit schematics, including:
- Autodesk AutoCAD: A popular CAD program that can be used to create detailed schematics.
- Microsoft Visio: A diagramming program that can be used to create schematics and other types of diagrams.
- SketchUp: A 3D modeling program that can be used to create detailed models of solar systems.
- PVSYST: A software program specifically designed for designing and simulating solar systems.
Conclusion
Designing and understanding home solar system circuit schematics is a complex task that requires careful consideration of several key components and design considerations. By following best practices and using standardized symbol sets, safety features, and scaling factors, you can create a safe and efficient solar system that meets your energy needs. Whether you are a professional solar installer or a DIY enthusiast, understanding solar system circuit schematics is essential for creating a reliable and efficient source of renewable energy.
Resources
For more information on designing and understanding home solar system circuit schematics, please refer to the following resources:
- National Electric Code (NEC): A set of standards for electrical systems, including solar systems.
- Underwriters Laboratories (UL): A safety certification organization that provides standards and testing for solar systems.
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): A global organization that provides standards for electrical systems, including solar systems.
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA): A trade association that provides resources and information on solar energy, including solar system design and installation.
Glossary
- AC (Alternating Current): A type of electricity that changes direction periodically.
- DC (Direct Current): A type of electricity that flows in one direction only.
- Inverter: A device that converts DC electricity into AC electricity.
- Charge Controller: A device that regulates the flow of energy from solar panels to batteries.
- Battery Bank: A group of batteries connected together to store energy.
- Load: A device or appliance that uses electricity, such as a light bulb or refrigerator.
By understanding the key components, design considerations, and best practices for creating a solar system circuit schematic, you can create a safe and efficient solar system that meets your energy needs and helps reduce your reliance on fossil fuels.


