Solar Panel Series-parallel Wiring Diagram
“Solar panel series-parallel wiring diagram”
One of the key components of a solar panel system is the wiring diagram, which determines how the panels are connected to each other and to the rest of the system. In this article, we will delve into the world of solar panel series-parallel wiring diagrams, exploring the benefits, limitations, and best practices for designing and implementing these systems.
Introduction to Solar Panel Wiring Diagrams
A solar panel wiring diagram is a visual representation of how the panels are connected to each other and to the rest of the system. The diagram shows the sequence of connections between the panels, the inverter, the charge controller, and the battery bank (if applicable). The wiring diagram is crucial in determining the overall efficiency, safety, and reliability of the solar panel system.
There are several types of solar panel wiring diagrams, including series, parallel, and series-parallel configurations. In this article, we will focus on series-parallel wiring diagrams, which offer a balance between the advantages of series and parallel configurations.
Series-Parallel Wiring Diagram: Definition and Benefits
A series-parallel wiring diagram is a configuration where multiple solar panels are connected in series to form a string, and multiple strings are connected in parallel to form an array. This configuration allows for a higher total voltage and current output, while also providing redundancy and flexibility in the system.
The benefits of a series-parallel wiring diagram include:
- Higher total voltage and current output: By connecting panels in series, the total voltage output of the string is increased, while the parallel connection of strings allows for a higher total current output.
- Improved reliability: If one panel in a string fails, the other panels in the string can continue to operate, reducing the impact of the failure on the overall system.
- Flexibility: Series-parallel configurations allow for easy addition or removal of panels, making it easier to upgrade or modify the system as needed.
- Reduced wiring requirements: By connecting panels in series, the number of wires required to connect the panels to the rest of the system is reduced, simplifying the installation process.

Components of a Series-Parallel Wiring Diagram
A series-parallel wiring diagram typically consists of the following components:
- Solar panels: The individual panels that make up the array, each with its own voltage and current rating.
- Strings: A group of panels connected in series to form a string, with a total voltage output equal to the sum of the individual panel voltages.
- Arrays: Multiple strings connected in parallel to form an array, with a total current output equal to the sum of the individual string currents.
- Inverter: A device that converts the DC power output of the solar panels to AC power, which can be fed into the grid or used to power loads.
- Charge controller: A device that regulates the flow of energy between the solar panels, battery bank, and load, preventing overcharging or undercharging of the batteries.
- Battery bank: A group of batteries that store excess energy generated by the solar panels during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight.
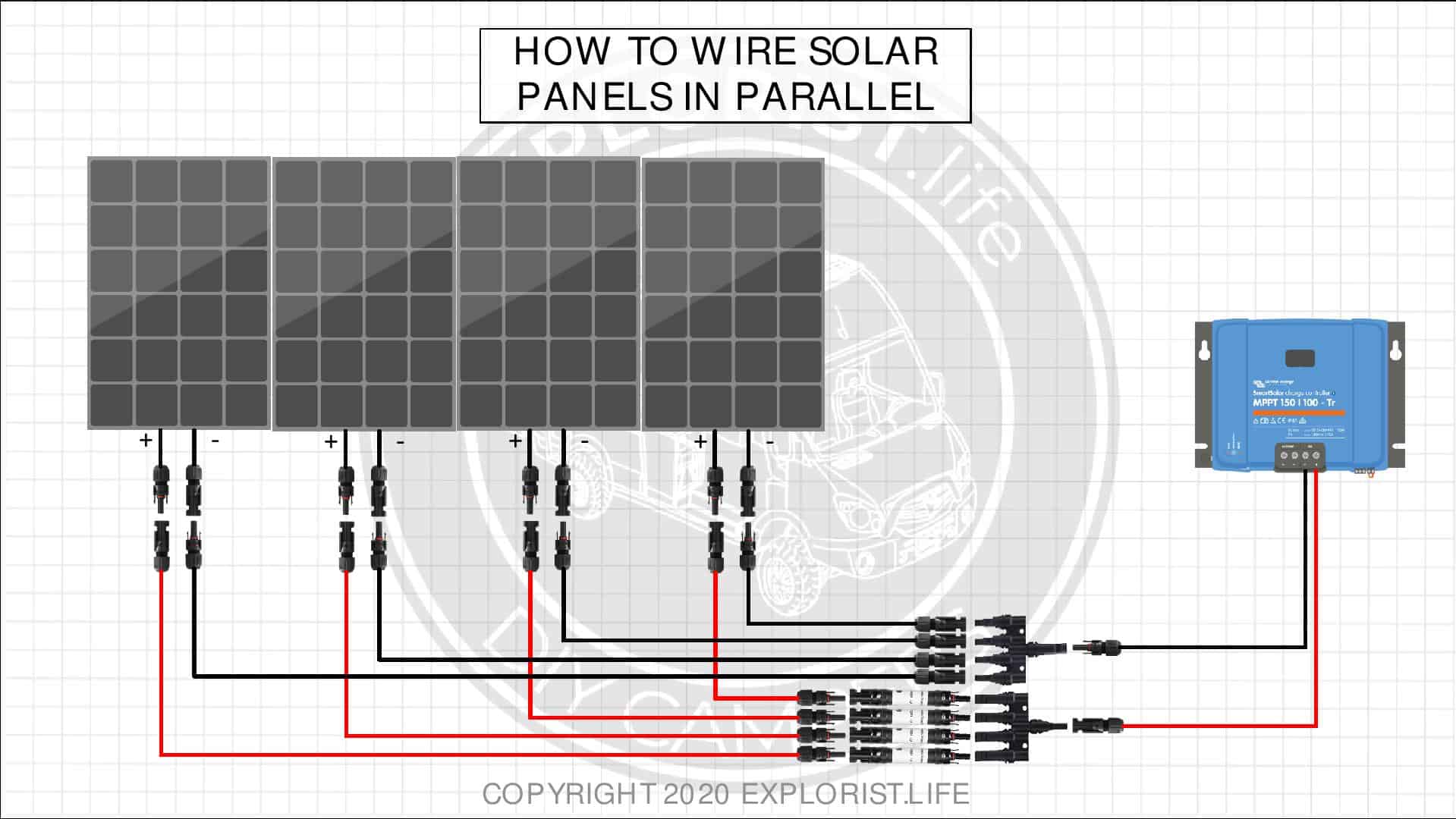
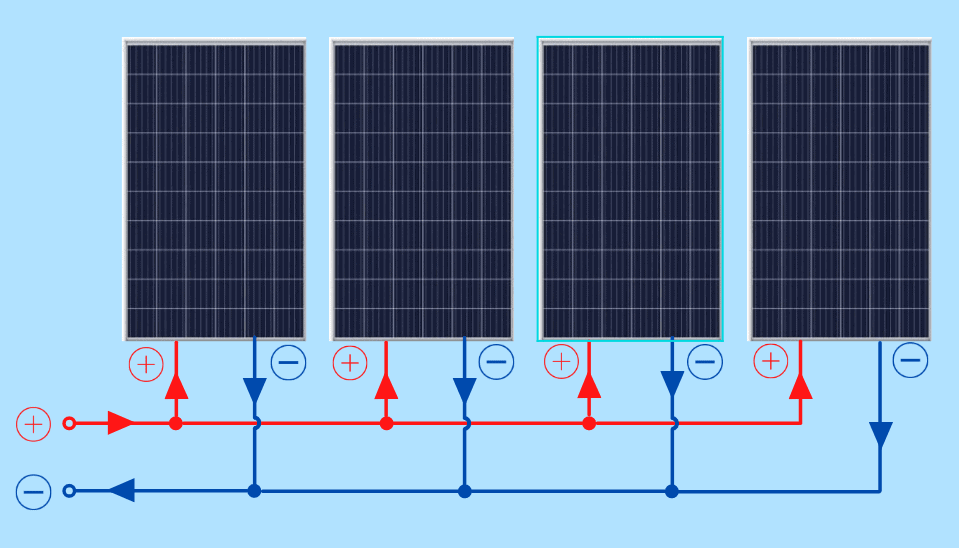
Designing a Series-Parallel Wiring Diagram
Designing a series-parallel wiring diagram requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Panel selection: Choosing panels with compatible voltage and current ratings to ensure efficient operation.
- String configuration: Determining the optimal number of panels per string to balance voltage and current output.
- Array configuration: Deciding the number of strings per array to achieve the desired total voltage and current output.
- Inverter selection: Choosing an inverter that can handle the total power output of the array, with a suitable voltage and current rating.
- Charge controller selection: Selecting a charge controller that can regulate the flow of energy between the solar panels, battery bank, and load.
Best Practices for Implementing a Series-Parallel Wiring Diagram
To ensure safe and efficient operation of a series-parallel wiring diagram, follow these best practices:
- Use compatible components: Ensure that all components, including panels, strings, arrays, inverters, and charge controllers, are compatible with each other in terms of voltage and current ratings.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for connecting and configuring the components.
- Use proper wiring and connections: Use high-quality wires and connectors to ensure reliable and efficient connections between components.
- Monitor and maintain the system: Regularly inspect and maintain the system to prevent damage, degradation, or malfunction.
- Consider expandability and upgradability: Design the system to allow for easy addition or removal of panels, strings, or arrays, as needed.
Challenges and Limitations of Series-Parallel Wiring Diagrams
While series-parallel wiring diagrams offer many benefits, they also present some challenges and limitations, including:
- Complexity: Series-parallel configurations can be more complex to design and implement than series or parallel configurations.
- Higher cost: The use of multiple strings and arrays can increase the overall cost of the system.
- Reduced efficiency: The parallel connection of strings can reduce the overall efficiency of the system, as the current output of each string may not be optimized.
- Increased risk of failure: The use of multiple components increases the risk of failure, which can impact the overall reliability of the system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a series-parallel wiring diagram is a popular configuration for solar panel systems, offering a balance between the advantages of series and parallel configurations. By understanding the benefits, limitations, and best practices for designing and implementing these systems, homeowners and businesses can create efficient, reliable, and cost-effective solar panel systems that meet their energy needs. Whether you are a seasoned solar panel installer or a DIY enthusiast, a series-parallel wiring diagram can help you harness the power of the sun and reduce your reliance on fossil fuels.
Recommendations for Future Development
As the solar panel industry continues to evolve, there are opportunities for future development and improvement in series-parallel wiring diagrams, including:
- Advancements in panel technology: Improvements in panel efficiency, durability, and affordability can further enhance the benefits of series-parallel configurations.
- Inverter and charge controller innovations: Advances in inverter and charge controller technology can improve the efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of series-parallel systems.
- System monitoring and control: The development of advanced system monitoring and control systems can enable real-time optimization of series-parallel configurations, improving overall efficiency and performance.
- Standardization and regulation: The establishment of industry standards and regulations can help ensure the safe and efficient implementation of series-parallel wiring diagrams.
By embracing these opportunities for future development, the solar panel industry can continue to innovate and improve, providing homeowners and businesses with even more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective solutions for harnessing the power of the sun.
