“Residential solar with battery backup wiring diagram”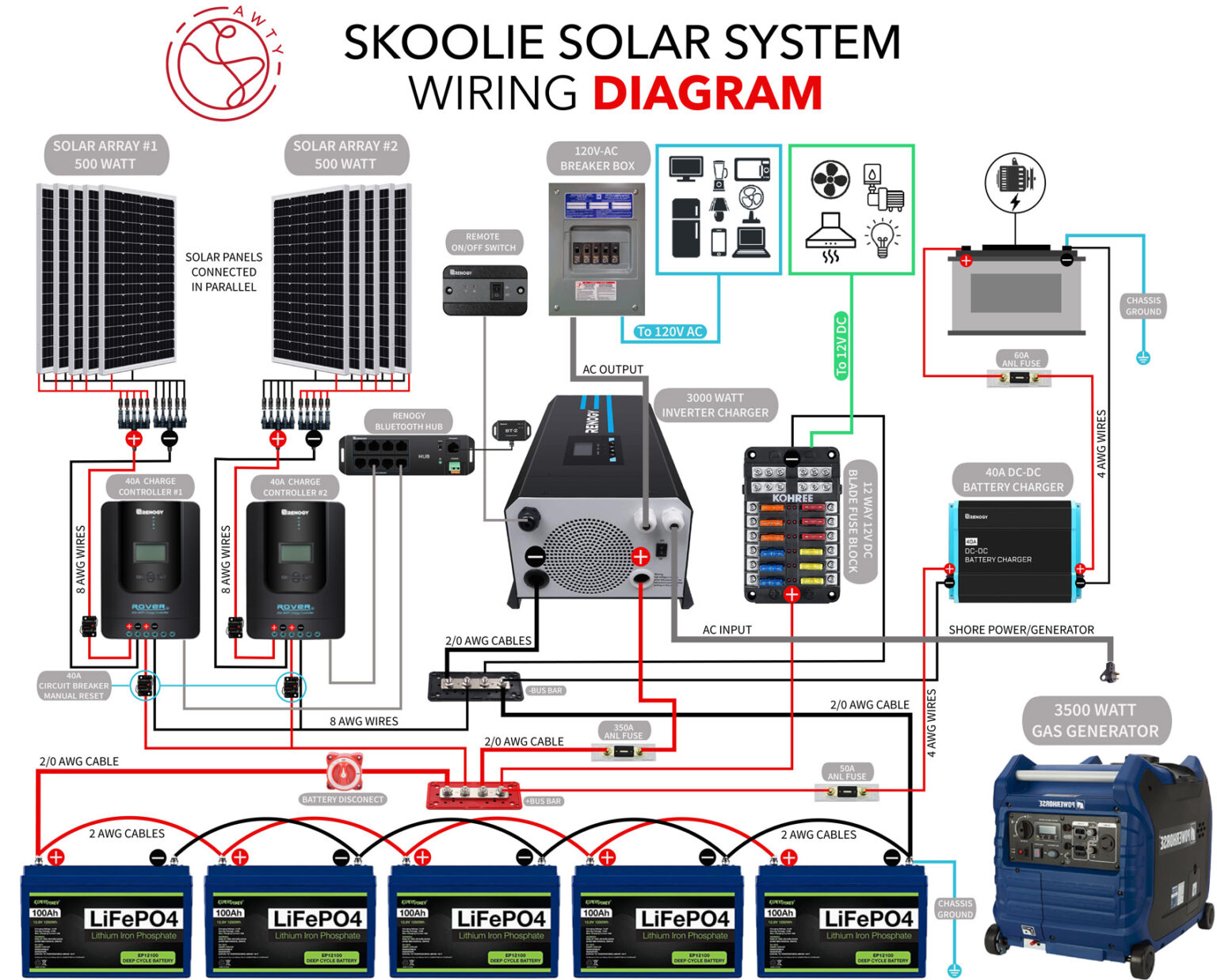
One of the most significant advantages of residential solar is the ability to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during power outages. This is made possible by integrating a battery backup system with your solar panel array. In this article, we will delve into the world of residential solar with battery backup, discuss the benefits, and provide a comprehensive wiring diagram to help you understand the system.
Introduction to Residential Solar
Residential solar systems, also known as photovoltaic (PV) systems, convert sunlight into electricity using solar panels. The solar panels are made up of photovoltaic cells that generate direct current (DC) electricity. The DC electricity is then sent to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity, making it usable in your home.
Benefits of Residential Solar
The benefits of residential solar are numerous:
- Reduced Energy Bills: Residential solar can significantly reduce your energy bills by generating free electricity from the sun.
- Increased Property Value: Installing a residential solar system can increase your property value, making it more attractive to potential buyers.
- Environmental Benefits: Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of energy, reducing your carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence: With a battery backup system, you can store excess energy for use during power outages or at night, providing energy independence.

Introduction to Battery Backup Systems
Battery backup systems, also known as energy storage systems, store excess energy generated by your solar panel array for later use. These systems typically consist of a battery bank, a charge controller, and an inverter. The battery bank stores the excess energy, the charge controller regulates the flow of energy, and the inverter converts the stored energy into usable AC electricity.
Benefits of Battery Backup Systems
The benefits of battery backup systems are:
- Energy Storage: Battery backup systems allow you to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during power outages.
- Increased Energy Independence: With a battery backup system, you can reduce your reliance on the grid and increase your energy independence.
- Backup Power: Battery backup systems provide backup power during grid outages, ensuring you have a reliable source of energy.
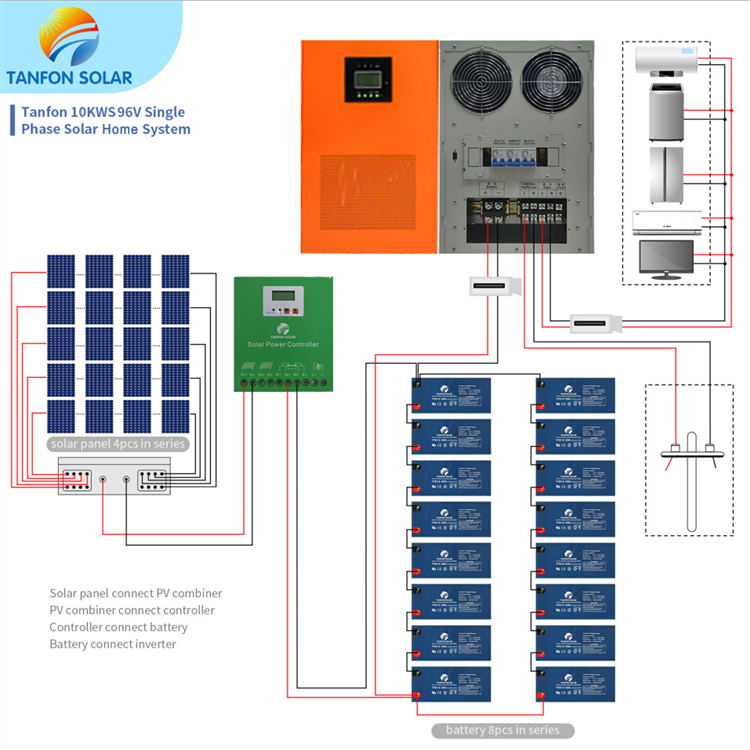
Wiring Diagram for Residential Solar with Battery Backup
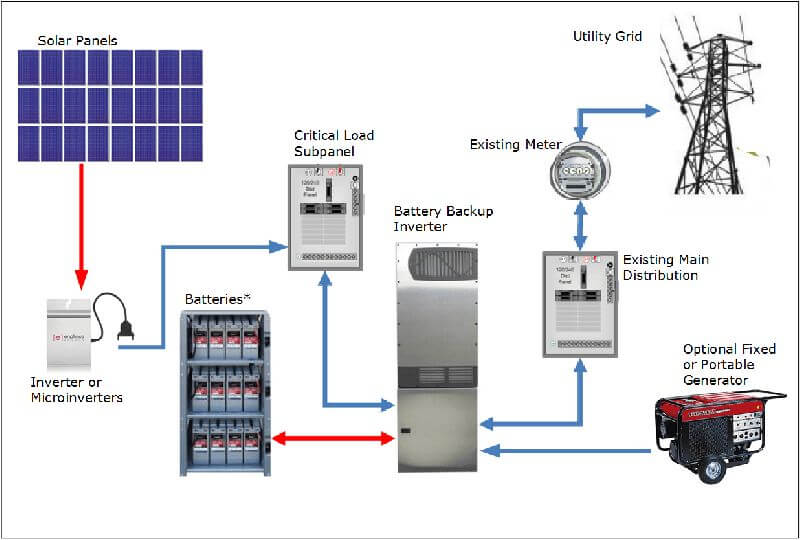
The following wiring diagram illustrates a typical residential solar system with battery backup:
System Components
- Solar Panel Array: The solar panel array consists of multiple solar panels connected in series and parallel to generate the desired voltage and current.
- Charge Controller: The charge controller regulates the flow of energy from the solar panel array to the battery bank.
- Battery Bank: The battery bank stores excess energy generated by the solar panel array.
- Inverter/Charger: The inverter/charger converts the stored energy in the battery bank into usable AC electricity and also charges the battery bank when the grid is available.
- Grid Tie Inverter: The grid tie inverter converts the DC electricity from the solar panel array into AC electricity and feeds it into the grid.
- Load Center: The load center is the main electrical panel that distributes power to the various loads in the home.
- Battery Backup Subpanel: The battery backup subpanel is a separate electrical panel that connects to the inverter/charger and provides backup power to critical loads.
Wiring Diagram
The wiring diagram is divided into three main sections:
Section 1: Solar Panel Array and Charge Controller
- The solar panel array is connected to the charge controller using MC4 connectors.
- The charge controller is connected to the battery bank using a battery cable.
Section 2: Battery Bank and Inverter/Charger
- The battery bank is connected to the inverter/charger using a battery cable.
- The inverter/charger is connected to the grid tie inverter using a 240V AC cable.
Section 3: Load Center and Battery Backup Subpanel
- The load center is connected to the grid tie inverter using a 240V AC cable.
- The battery backup subpanel is connected to the inverter/charger using a 240V AC cable.
- Critical loads such as lights, refrigerator, and computer are connected to the battery backup subpanel.
System Operation
The system operates in three modes:
- Grid Tie Mode: During the day, the solar panel array generates electricity and feeds it into the grid through the grid tie inverter. Excess energy is stored in the battery bank.
- Battery Backup Mode: During the night or during a grid outage, the inverter/charger converts the stored energy in the battery bank into usable AC electricity and supplies it to the critical loads.
- Grid Backup Mode: When the grid is available, the inverter/charger charges the battery bank from the grid.
Conclusion
Residential solar with battery backup is a reliable and efficient way to generate and store energy. By understanding the benefits and components of a residential solar system with battery backup, you can make an informed decision about installing a system in your home. The wiring diagram provided in this article illustrates a typical system configuration and can serve as a reference for installers and homeowners. With the increasing popularity of residential solar, it’s essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the system components, benefits, and wiring diagram to ensure a safe and efficient installation.
Additional Resources
For those interested in learning more about residential solar with battery backup, the following resources are recommended:
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) – www.nrel.gov
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) – www.seia.org
- International Association of Electrical Inspectors (IAEI) – www.iaei.org
Glossary
- AC (Alternating Current): A type of electric current that periodically reverses direction.
- DC (Direct Current): A type of electric current that flows in one direction.
- Grid Tie Inverter: An inverter that converts DC electricity from the solar panel array into AC electricity and feeds it into the grid.
- Inverter/Charger: An inverter that converts the stored energy in the battery bank into usable AC electricity and also charges the battery bank when the grid is available.
- MC4 Connectors: A type of connector used to connect solar panels to the charge controller.
- Photovoltaic (PV) Cells: Cells that convert sunlight into electricity.
By understanding the components, benefits, and wiring diagram of a residential solar system with battery backup, you can make an informed decision about installing a system in your home and enjoy the benefits of renewable energy.


