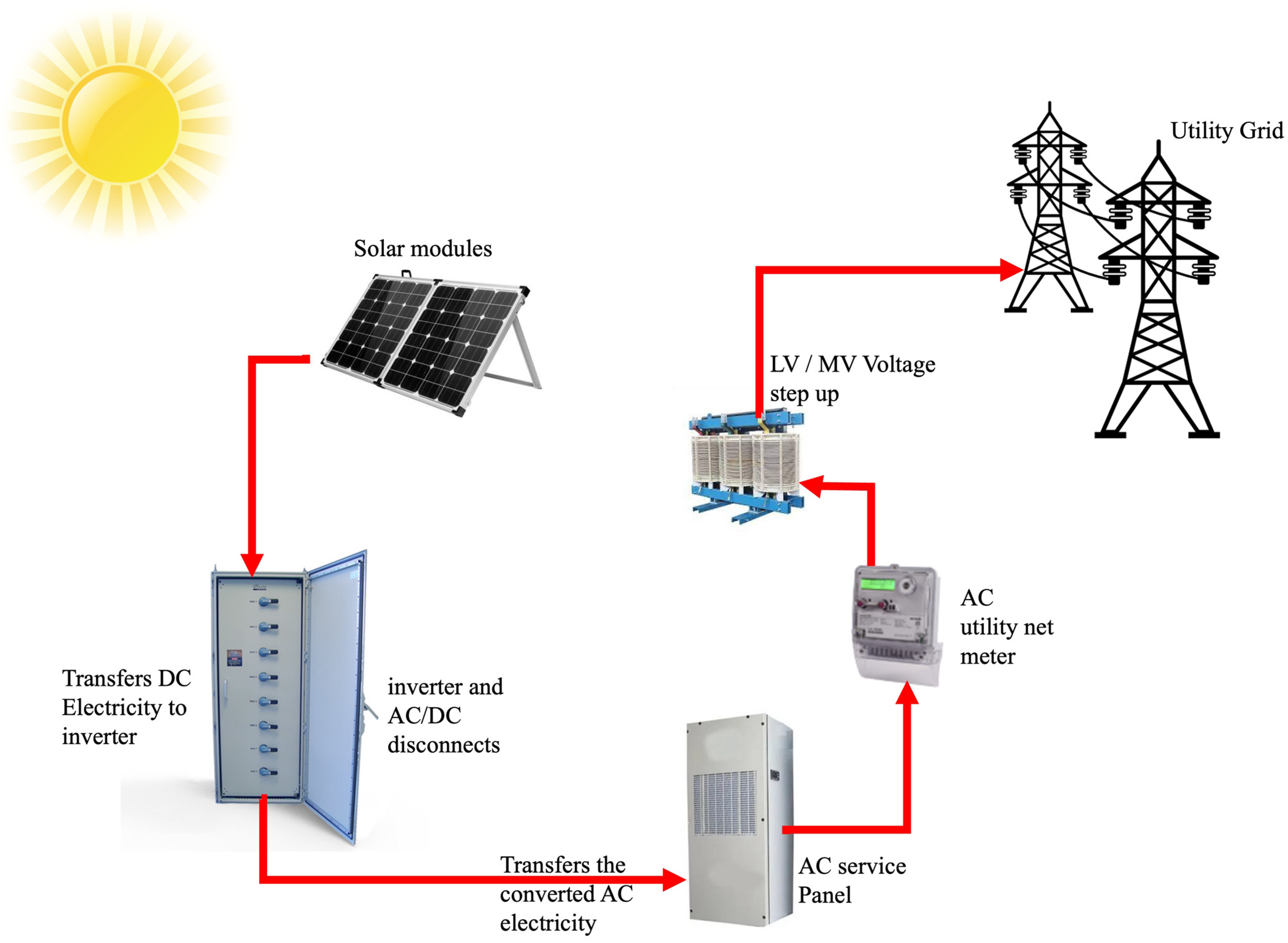
“Grid-tied solar power system wiring schematic”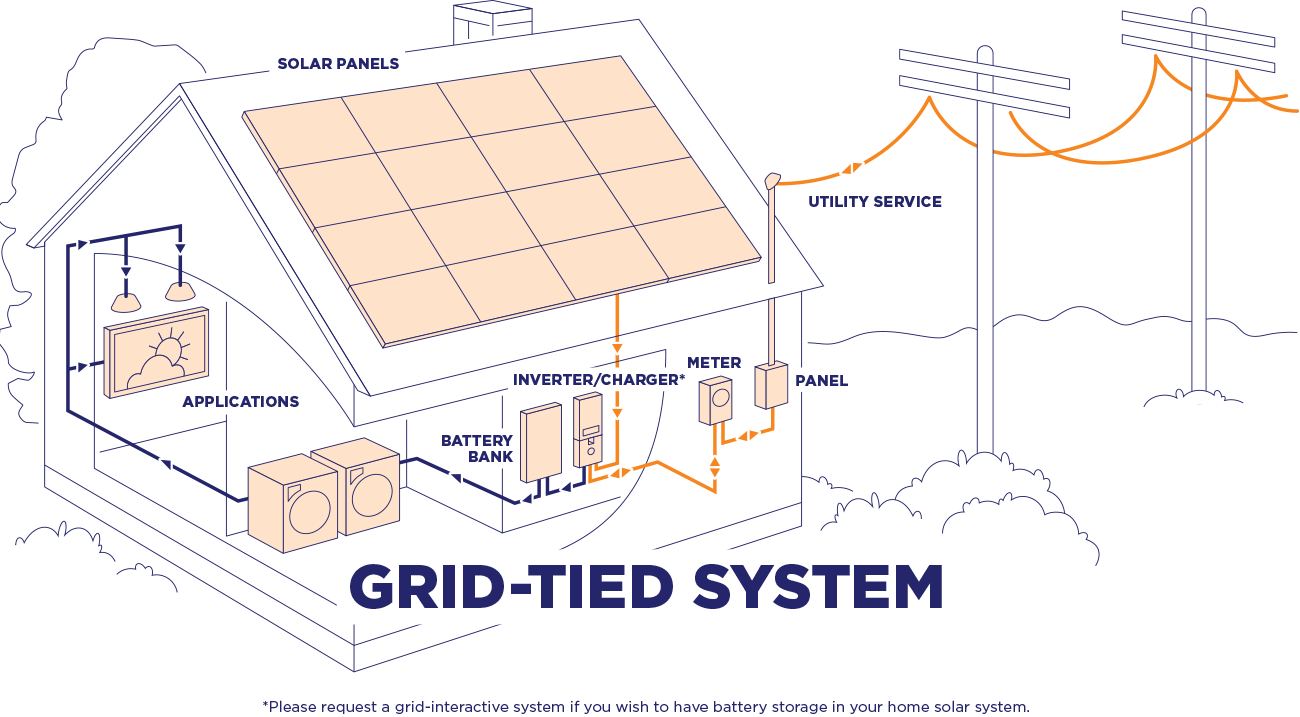
A grid-tied solar power system is a type of solar panel system that is connected to the main electrical grid, allowing homeowners to generate their own electricity and sell any excess energy back to the utility company. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to grid-tied solar power system wiring schematics, including the components, installation process, and safety considerations.
Introduction to Grid-tied Solar Power Systems
A grid-tied solar power system consists of several key components, including solar panels, a mounting system, an inverter, and a net meter. The solar panels convert sunlight into DC electricity, which is then sent to the inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity, which is then fed into the main electrical grid. The net meter measures the amount of energy generated by the solar panel system and the amount of energy consumed by the household.
Components of a Grid-tied Solar Power System
The following are the main components of a grid-tied solar power system:
- Solar Panels: Solar panels are the primary component of a solar power system, converting sunlight into DC electricity. They are typically installed on the roof or in a ground-mounted array.
- Mounting System: The mounting system is used to secure the solar panels to the roof or ground. It consists of a frame, clamps, and anchors that are designed to withstand wind and weather conditions.
- Inverter: The inverter is a critical component of a grid-tied solar power system, converting DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity that can be fed into the main electrical grid.
- Net Meter: The net meter measures the amount of energy generated by the solar panel system and the amount of energy consumed by the household. It is typically installed between the solar panel system and the main electrical panel.
- Main Electrical Panel: The main electrical panel is the central distribution point for the household’s electrical system. It is where the solar panel system is connected to the main electrical grid.

Wiring Schematic for a Grid-tied Solar Power System
The wiring schematic for a grid-tied solar power system is complex and requires careful planning and installation. The following is a general overview of the wiring schematic:
- Solar Panel Array: The solar panel array is connected in a series-parallel configuration, with each string of panels connected to a combiner box.
- Combiner Box: The combiner box is used to combine the output of multiple strings of solar panels into a single output.
- Inverter: The inverter is connected to the combiner box and converts the DC electricity from the solar panel array into AC electricity.
- Net Meter: The net meter is connected to the inverter and measures the amount of energy generated by the solar panel system.
- Main Electrical Panel: The main electrical panel is connected to the net meter and is the central distribution point for the household’s electrical system.


Installation Process
The installation process for a grid-tied solar power system involves several steps, including:
- Site Assessment: A site assessment is conducted to determine the suitability of the location for a solar panel system.
- System Design: The system is designed to meet the energy needs of the household, taking into account the amount of sunlight available and the electrical requirements of the household.
- Component Installation: The components of the system, including the solar panels, mounting system, inverter, and net meter, are installed.
- Wiring and Connections: The wiring and connections are made, including the connection to the main electrical panel.
- Testing and Commissioning: The system is tested and commissioned to ensure that it is functioning correctly and safely.
Safety Considerations
Safety is a critical consideration when installing a grid-tied solar power system. The following are some safety considerations to keep in mind:
- Electrical Shock: Electrical shock is a risk when working with electrical systems. Ensure that all components are properly grounded and that the system is installed by a qualified electrician.
- Fire Risk: Fire is a risk when working with electrical systems. Ensure that all components are properly installed and maintained to minimize the risk of fire.
- Fall Protection: Fall protection is critical when working at heights. Ensure that all personnel are properly trained and equipped to work at heights.
- Personal Protective Equipment: Personal protective equipment, including hard hats, safety glasses, and gloves, should be worn at all times when working on a solar panel system.
Code Compliance
Code compliance is critical when installing a grid-tied solar power system. The following are some code requirements to keep in mind:
- National Electrical Code (NEC): The NEC is the national standard for electrical safety in the United States. Ensure that all components and installation practices meet NEC requirements.
- Local Building Codes: Local building codes may have specific requirements for solar panel systems. Ensure that all components and installation practices meet local building code requirements.
- Utility Company Requirements: Utility companies may have specific requirements for grid-tied solar power systems. Ensure that all components and installation practices meet utility company requirements.
Conclusion
A grid-tied solar power system is a complex electrical system that requires careful planning, installation, and maintenance. The wiring schematic for a grid-tied solar power system is critical to ensuring that the system functions safely and efficiently. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, homeowners and installers can ensure that their grid-tied solar power system is installed correctly and meets all relevant code requirements. Remember to always follow safety protocols and best practices when working with electrical systems, and consult with a qualified electrician if you are unsure about any aspect of the installation process.
Appendix
The following is a sample wiring schematic for a grid-tied solar power system:
- Solar Panel Array:
- String 1: Panel 1 + Panel 2 + Panel 3
- String 2: Panel 4 + Panel 5 + Panel 6
- Combiner Box:
- Input: String 1 + String 2
- Output: DC Electricity
- Inverter:
- Input: DC Electricity from Combiner Box
- Output: AC Electricity
- Net Meter:
- Input: AC Electricity from Inverter
- Output: Energy Measurement
- Main Electrical Panel:
- Input: AC Electricity from Net Meter
- Output: Household Electrical System
Note: This is a simplified example and actual wiring schematics may vary depending on the specific system design and installation requirements.
References
- National Electrical Code (NEC)
- Local Building Codes
- Utility Company Requirements
- Manufacturer’s Instructions
- Industry Best Practices
By following the guidelines outlined in this article and consulting with relevant references, homeowners and installers can ensure that their grid-tied solar power system is installed correctly and meets all relevant code requirements.