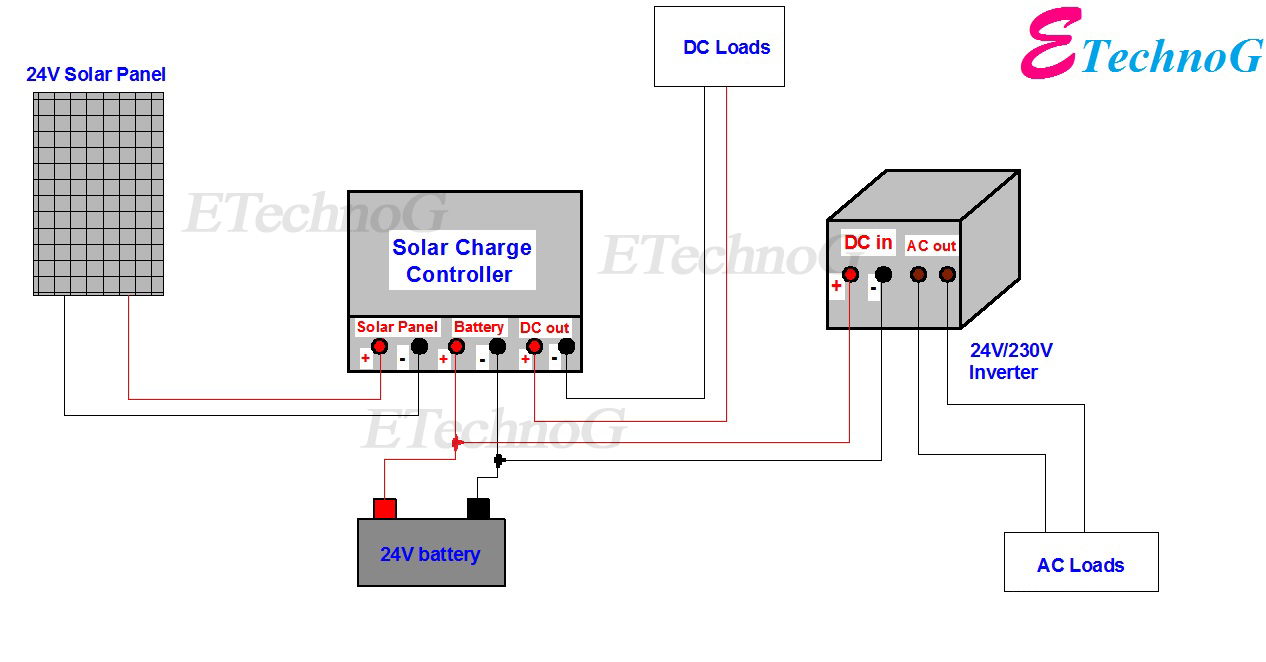
“Residential solar system wiring layout with charge controller”
A well-designed solar system wiring layout is crucial for ensuring the efficient and safe operation of a residential solar power system. In this article, we will delve into the details of designing a residential solar system wiring layout with a charge controller, exploring the key components, best practices, and essential considerations.
Introduction to Residential Solar Systems
A residential solar system typically consists of solar panels, a charge controller, a battery bank, and an inverter. The solar panels generate DC power from sunlight, which is then regulated by the charge controller and stored in the battery bank. The inverter converts the DC power to AC power, making it usable for household appliances.
Importance of a Well-Designed Wiring Layout
A well-designed wiring layout is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a residential solar system. A poorly designed wiring layout can lead to reduced system performance, increased energy losses, and even electrical shock or fires. A good wiring layout should be easy to install, maintain, and troubleshoot, with clear labeling and documentation.
Key Components of a Residential Solar System Wiring Layout
- Solar Panels: The solar panels are the primary source of power in a residential solar system. They are typically connected in series and/or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and current.
- Charge Controller: The charge controller regulates the flow of energy from the solar panels to the battery bank, preventing overcharging and ensuring the battery bank is fully charged.
- Battery Bank: The battery bank stores excess energy generated by the solar panels during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight.
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC power from the battery bank to AC power, making it usable for household appliances.
- Wiring and Connectors: The wiring and connectors used in a residential solar system must be designed to withstand the outdoor environment and ensure reliable connections between components.

Designing a Residential Solar System Wiring Layout with a Charge Controller
When designing a residential solar system wiring layout with a charge controller, the following steps should be followed:
- Determine the System Requirements: Determine the total power requirements of the household, including the number of appliances, lighting, and other electrical loads.
- Select the Solar Panel Array: Select a solar panel array that meets the system requirements, taking into account the available roof space, solar irradiance, and local building codes.
- Choose a Charge Controller: Choose a charge controller that is compatible with the solar panel array and battery bank, and can handle the maximum power output of the solar panels.
- Design the Battery Bank: Design the battery bank to meet the system requirements, taking into account the depth of discharge, battery type, and charging/discharging cycles.
- Select the Inverter: Select an inverter that is compatible with the battery bank and can handle the maximum power output of the solar panels.
- Plan the Wiring Layout: Plan the wiring layout to ensure that all components are connected correctly, with clear labeling and documentation.
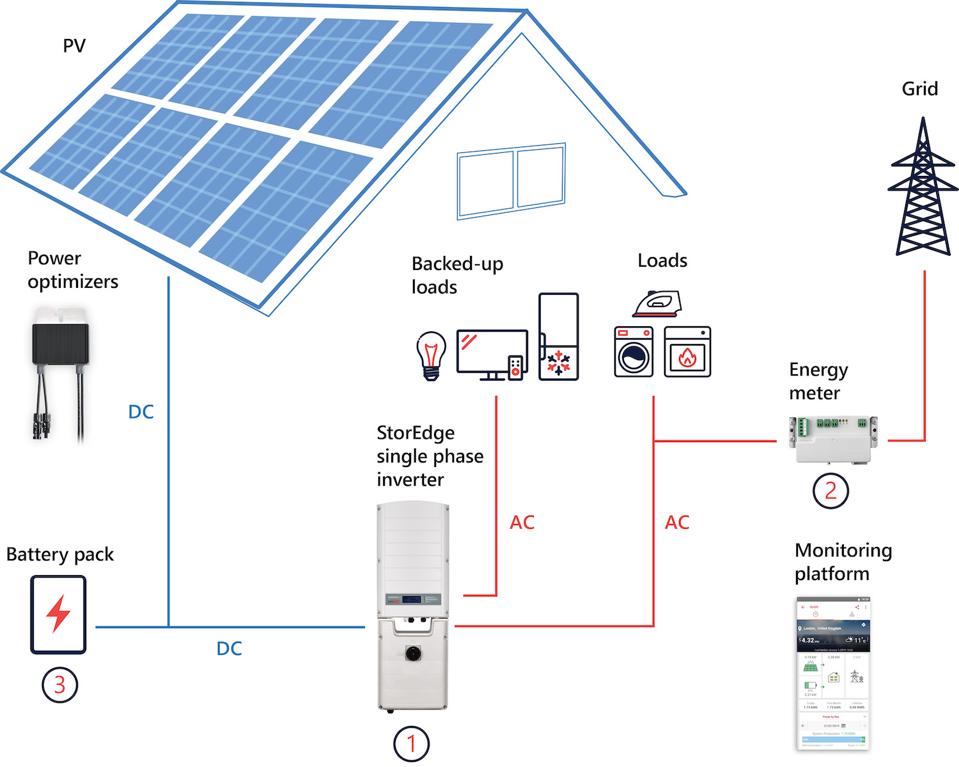
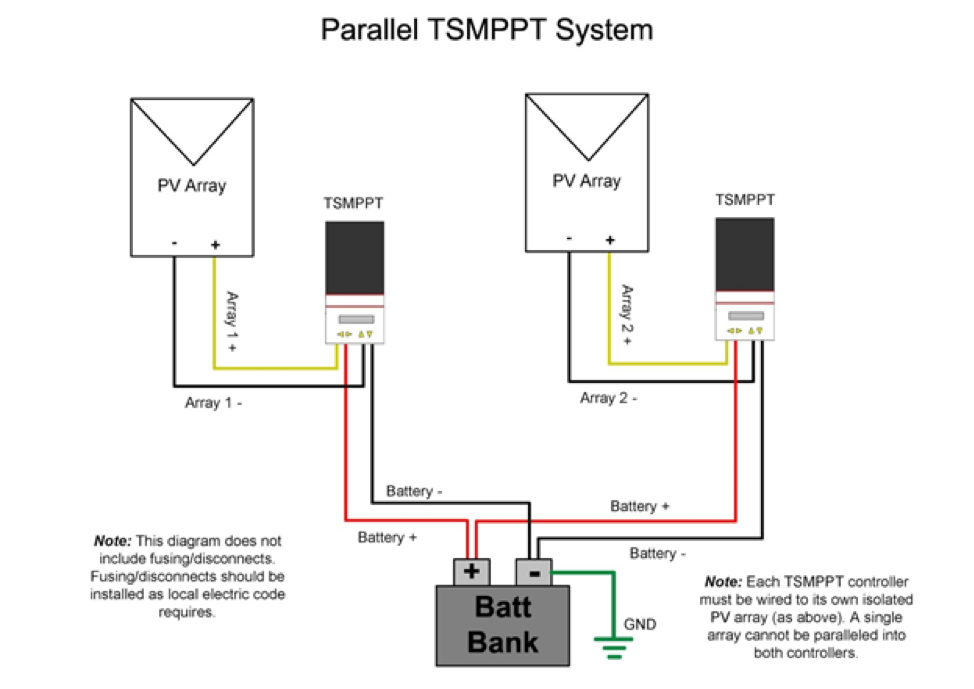
Best Practices for Residential Solar System Wiring Layout
- Use Color-Coded Wiring: Use color-coded wiring to identify different components and wiring paths, making it easier to troubleshoot and maintain the system.
- Label All Components: Label all components, including solar panels, charge controllers, battery banks, and inverters, to ensure clear identification.
- Use Weatherproof Connectors: Use weatherproof connectors to protect the wiring from the outdoor environment and ensure reliable connections.
- Keep Wiring Runs Short: Keep wiring runs short to minimize energy losses and reduce the risk of electrical shock or fires.
- Use Grounding and Bonding: Use grounding and bonding to ensure the safe operation of the system and protect against electrical shock.
Essential Considerations for Residential Solar System Wiring Layout
- Compliance with Local Building Codes: Ensure that the wiring layout complies with local building codes and regulations, including the National Electric Code (NEC).
- System Monitoring and Maintenance: Ensure that the system is designed for easy monitoring and maintenance, with clear labeling and documentation.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Ensure that the system is designed to be scalable and flexible, allowing for future upgrades or expansions.
- Energy Efficiency: Ensure that the system is designed to maximize energy efficiency, minimizing energy losses and reducing the carbon footprint.
- Safety: Ensure that the system is designed with safety in mind, protecting against electrical shock, fires, and other hazards.
Conclusion
Designing a residential solar system wiring layout with a charge controller requires careful consideration of the key components, best practices, and essential considerations. A well-designed wiring layout is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a residential solar power system, maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing energy losses. By following the steps outlined in this article, homeowners and solar installers can create a reliable and efficient residential solar system that meets their energy needs and contributes to a sustainable future.
Recommended Tools and Materials
- Solar Panel Array: Select a solar panel array that meets the system requirements, taking into account the available roof space, solar irradiance, and local building codes.
- Charge Controller: Choose a charge controller that is compatible with the solar panel array and battery bank, and can handle the maximum power output of the solar panels.
- Battery Bank: Design the battery bank to meet the system requirements, taking into account the depth of discharge, battery type, and charging/discharging cycles.
- Inverter: Select an inverter that is compatible with the battery bank and can handle the maximum power output of the solar panels.
- Wiring and Connectors: Use weatherproof connectors and color-coded wiring to ensure reliable connections and easy identification.
- Grounding and Bonding Equipment: Use grounding and bonding equipment to ensure the safe operation of the system and protect against electrical shock.
Additional Resources
- National Electric Code (NEC): Ensure that the wiring layout complies with the NEC, which provides guidelines for the safe installation of electrical systems.
- Local Building Codes: Ensure that the wiring layout complies with local building codes and regulations, which may vary depending on the location.
- Solar Industry Associations: Consult with solar industry associations, such as the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), for guidance on designing and installing residential solar systems.
- Manufacturer Instructions: Follow the manufacturer instructions for each component, including solar panels, charge controllers, battery banks, and inverters.
By following the guidelines outlined in this article, homeowners and solar installers can create a reliable and efficient residential solar system that meets their energy needs and contributes to a sustainable future.