“Residential solar power wiring schematics”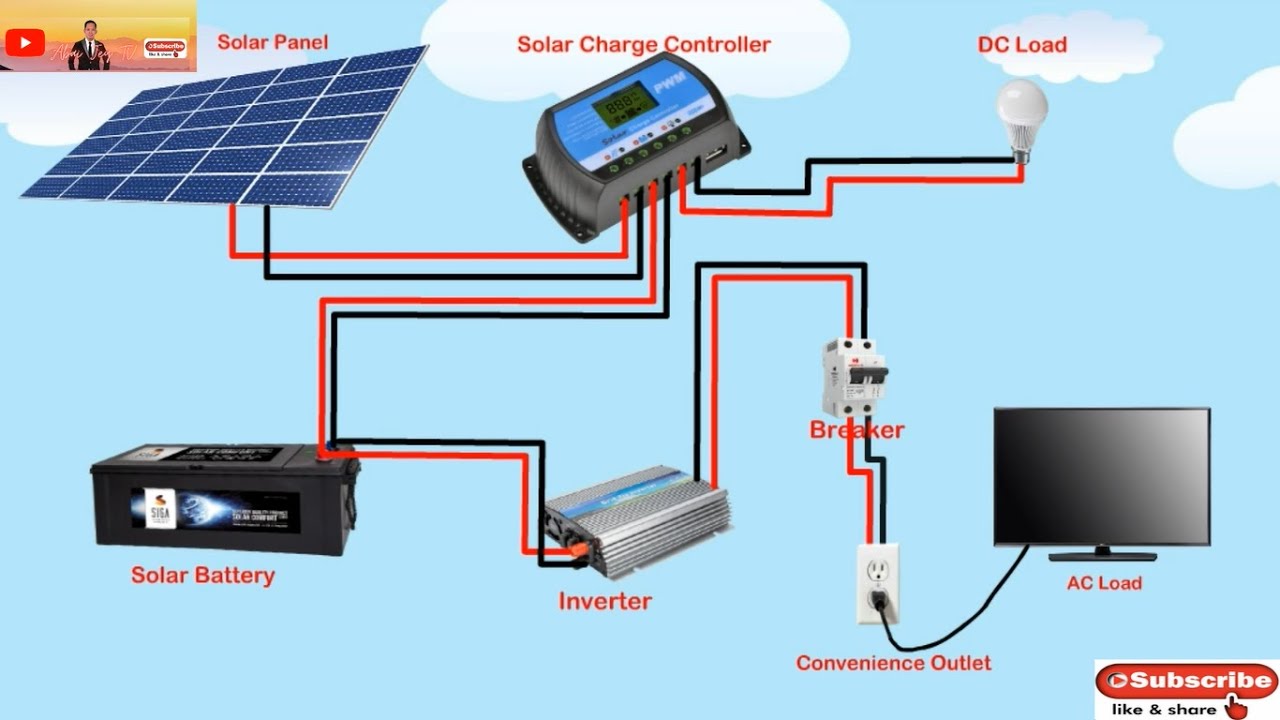
With the growing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solutions, homeowners are turning to solar power to reduce their carbon footprint and save on energy costs. One crucial aspect of installing a residential solar power system is the wiring schematics. In this article, we will delve into the world of residential solar power wiring schematics, exploring the fundamentals, components, and best practices for designing and implementing a safe and efficient solar power system.
Introduction to Residential Solar Power Systems
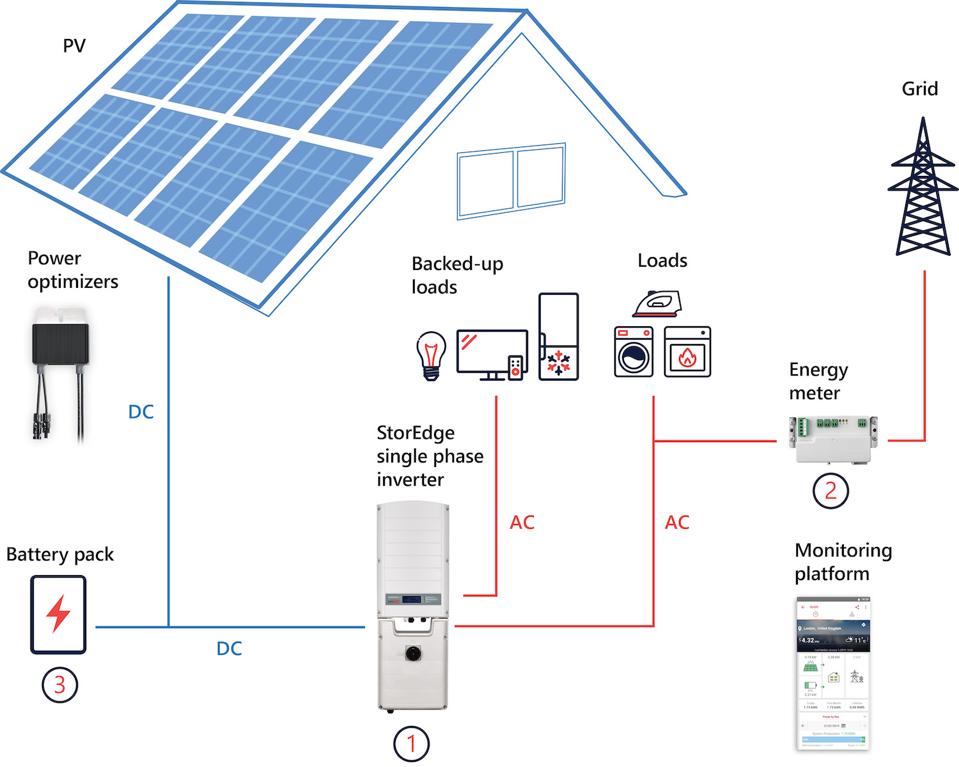
A residential solar power system is a network of components that work together to generate electricity from sunlight. The system typically consists of solar panels, an inverter, a mounting system, and a wiring system. The solar panels convert sunlight into DC (direct current) electricity, which is then sent to the inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity into AC (alternating current) electricity, which is compatible with the electrical grid and can power appliances in the home.
Wiring Schematics: The Blueprint for a Safe and Efficient System
Wiring schematics are the detailed diagrams that illustrate the electrical connections between components in a solar power system. These diagrams are essential for ensuring that the system is designed and installed correctly, meeting all safety and performance standards. A well-designed wiring schematic will help to:
- Prevent electrical shock and fires: A properly designed wiring system will minimize the risk of electrical shock and fires, protecting people and property.
- Optimize system performance: A well-designed wiring system will ensure that the solar power system operates at maximum efficiency, generating the most electricity possible from the available sunlight.
- Reduce maintenance and repair costs: A clear and comprehensive wiring schematic will make it easier to identify and troubleshoot issues, reducing maintenance and repair costs over the life of the system.
Components of a Residential Solar Power Wiring Schematic

A residential solar power wiring schematic will typically include the following components:
- Solar panels: The solar panels are the primary components of the system, converting sunlight into DC electricity.
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity, compatible with the electrical grid.
- Mounting system: The mounting system secures the solar panels to the roof or ground, ensuring a stable and durable installation.
- Wiring and connectors: The wiring and connectors connect the solar panels, inverter, and other components, facilitating the flow of electricity.
- Grounding system: The grounding system provides a safe path for electrical current to flow to the ground, protecting people and equipment from electrical shock.
- Overcurrent protection devices: Overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses and circuit breakers, protect the system from electrical overloads and surges.
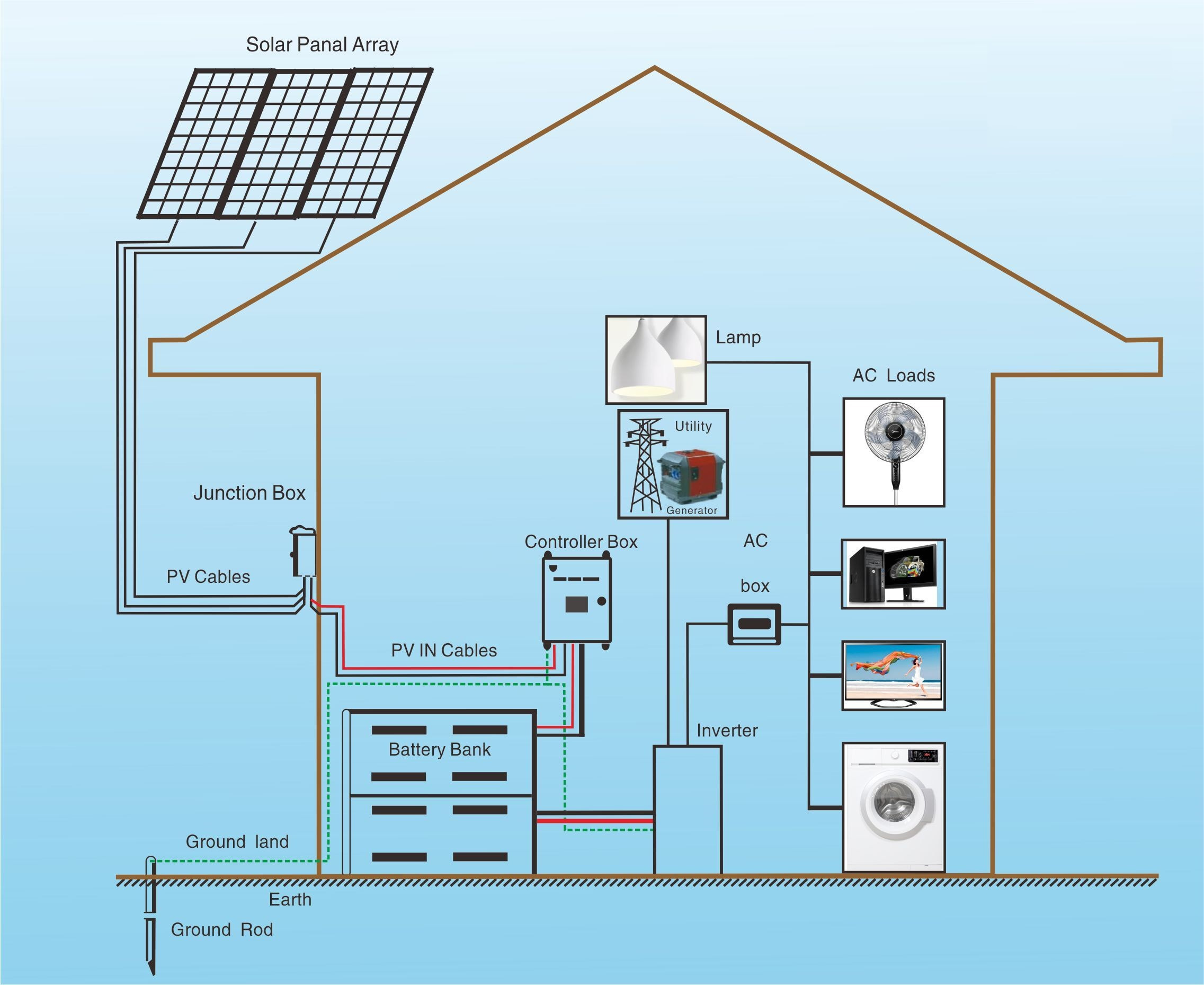
Designing a Residential Solar Power Wiring Schematic
Designing a residential solar power wiring schematic requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- System size and configuration: The size and configuration of the solar power system will determine the type and number of components required.
- Electrical codes and standards: The wiring schematic must comply with local electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electric Code (NEC) in the United States.
- Component specifications: The specifications of the solar panels, inverter, and other components will influence the design of the wiring schematic.
- System monitoring and control: The wiring schematic may include provisions for system monitoring and control, such as remote monitoring and energy management systems.
Best Practices for Implementing a Residential Solar Power Wiring Schematic
To ensure a safe and efficient residential solar power system, follow these best practices when implementing a wiring schematic:
- Hire a qualified electrician: A qualified electrician with experience in solar power systems should design and install the wiring schematic.
- Use high-quality components: Use high-quality components, such as solar panels and inverters, that meet or exceed industry standards.
- Follow electrical codes and standards: Ensure that the wiring schematic complies with local electrical codes and standards.
- Test and commission the system: Thoroughly test and commission the system to ensure that it operates safely and efficiently.
- Maintain accurate documentation: Maintain accurate documentation of the wiring schematic, including diagrams, specifications, and test results.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Despite careful design and implementation, issues can arise with a residential solar power wiring schematic. Some common issues include:
- Electrical overloads and surges: Overcurrent protection devices can help prevent electrical overloads and surges.
- Grounding issues: A proper grounding system is essential for protecting people and equipment from electrical shock.
- Component failures: Regular maintenance and inspection can help identify and replace faulty components.
- System monitoring and control issues: Ensure that system monitoring and control systems are properly configured and maintained.
Conclusion
Residential solar power wiring schematics are a critical component of a safe and efficient solar power system. By understanding the fundamentals, components, and best practices for designing and implementing a wiring schematic, homeowners and installers can ensure a reliable and high-performing system. Remember to hire a qualified electrician, use high-quality components, follow electrical codes and standards, and maintain accurate documentation to ensure a successful installation. With a well-designed and implemented wiring schematic, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of renewable energy while minimizing the risks associated with electrical systems.
Additional Resources
For those seeking additional information on residential solar power wiring schematics, the following resources are recommended:
- National Electric Code (NEC): A comprehensive guide to electrical codes and standards in the United States.
- International Association of Electrical Inspectors (IAEI): A professional organization providing resources and training for electrical inspectors and installers.
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA): A trade association providing resources and information on solar energy and solar power systems.
- Local electrical authorities: Contact local electrical authorities for specific codes, standards, and regulations in your area.
By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, homeowners and installers can create a safe and efficient residential solar power system that meets their energy needs while minimizing their environmental impact.


