“How are residential solar systems wired?”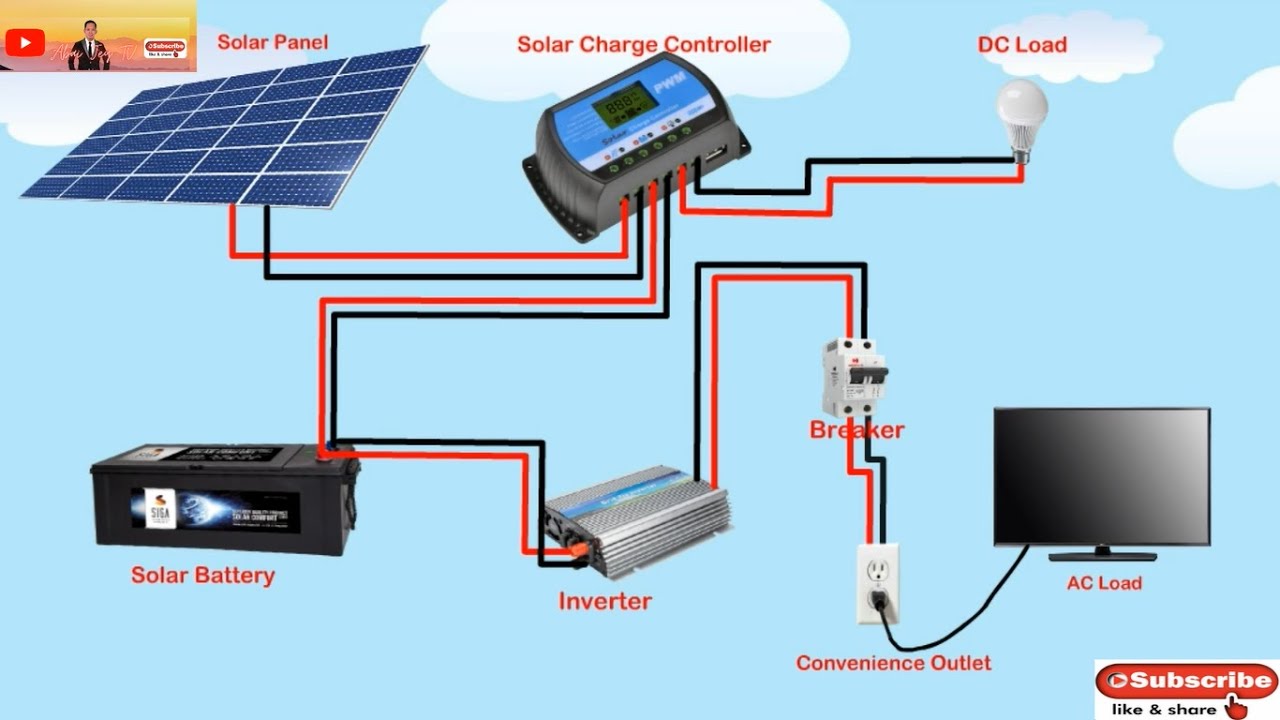
Not only do they help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, but they also provide a cost-effective and sustainable way to power our homes. However, have you ever wondered how these systems are wired? In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of residential solar system wiring, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the process.
Introduction to Residential Solar Systems
Before we dive into the wiring aspect, let’s take a brief look at how residential solar systems work. A typical residential solar system consists of several key components, including:
- Solar Panels: These are the photovoltaic (PV) modules that convert sunlight into electrical energy.
- Inverter: This device converts the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power, which is usable in your home.
- Mounting System: This includes the racks, clamps, and other hardware that secure the solar panels to your roof.
- Electrical Panel: This is the main distribution panel that receives the AC power from the inverter and distributes it throughout your home.
Wiring Components
Now, let’s explore the wiring components that connect these key elements. The wiring system in a residential solar installation typically consists of:

- PV Cables: These are the cables that connect the solar panels to the inverter. They are usually DC-rated and designed to withstand the high temperatures and outdoor conditions.
- Inverter Cables: These cables connect the inverter to the electrical panel and are typically AC-rated.
- Grounding Cables: These cables provide a safe path to ground for the electrical current, ensuring the system is properly grounded and protected against electrical shocks.
- Disconnects: These are specialized switches that allow you to disconnect the solar system from the grid or inverter for maintenance or repair purposes.

Wiring Configurations
There are several wiring configurations used in residential solar systems, including:
- Series Wiring: In this configuration, the solar panels are wired in series, with each panel connected to the next in a single string. This configuration is suitable for smaller systems with fewer panels.
- Parallel Wiring: In this configuration, multiple strings of solar panels are wired in parallel, allowing for more flexibility and scalability.
- Combination of Series and Parallel: This configuration combines the benefits of both series and parallel wiring, allowing for multiple strings of panels to be connected in parallel.

Wiring Best Practices
To ensure a safe and efficient residential solar system, it’s essential to follow best practices when it comes to wiring. These include:
- Using the Correct Wire Size: The wire size should be sufficient to handle the maximum current output of the solar panels and inverter.
- Keeping Wires Organized: Wires should be neatly labeled and organized to prevent confusion and ensure easy maintenance.
- Securing Wires: Wires should be securely fastened to the roof or other structures to prevent damage from wind, weather, or other external factors.
- Testing and Inspecting: The wiring system should be thoroughly tested and inspected before the system is commissioned to ensure it meets local electrical codes and standards.
Code Compliance
Residential solar systems must comply with local electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electric Code (NEC) in the United States. These codes dictate the minimum requirements for wiring, grounding, and electrical safety. Some key code compliance considerations include:
- Grounding and Bonding: The solar system must be properly grounded and bonded to ensure electrical safety and prevent shock hazards.
- Arc Fault Protection: The system must include arc fault protection devices to prevent electrical fires and shocks.
- Disconnects and Switches: The system must include disconnects and switches that meet specific code requirements for safety and maintenance.
Installation and Maintenance
The installation and maintenance of residential solar systems require specialized knowledge and expertise. It’s essential to hire a qualified and licensed solar installer who follows best practices and code compliance guidelines. Some key installation and maintenance considerations include:
- Initial Installation: The system should be installed according to the manufacturer’s instructions and local electrical codes.
- Regular Maintenance: The system should be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure optimal performance and extend its lifespan.
- Troubleshooting: The installer should be able to troubleshoot and repair any issues that arise during installation or maintenance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, residential solar systems require careful planning, design, and installation to ensure safe and efficient operation. The wiring system is a critical component of the overall system, and it’s essential to follow best practices and code compliance guidelines to ensure electrical safety and prevent shock hazards. By understanding the intricacies of residential solar system wiring, homeowners can make informed decisions when it comes to installing and maintaining their solar systems. Whether you’re a homeowner, installer, or industry professional, this comprehensive guide has provided you with a detailed understanding of the wiring aspects of residential solar systems.
Additional Resources
For those interested in learning more about residential solar systems and wiring, here are some additional resources:
- National Electric Code (NEC): The NEC provides guidelines for electrical safety and code compliance.
- International Association of Electrical Inspectors (IAEI): The IAEI offers training and resources for electrical inspectors and professionals.
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA): The SEIA provides information and resources on solar energy and industry best practices.
- Local Electrical Codes and Standards: Homeowners and installers should consult local electrical codes and standards for specific requirements and guidelines.
By staying informed and up-to-date on the latest industry developments and best practices, we can ensure the safe and efficient operation of residential solar systems, while promoting the growth and adoption of renewable energy sources.


