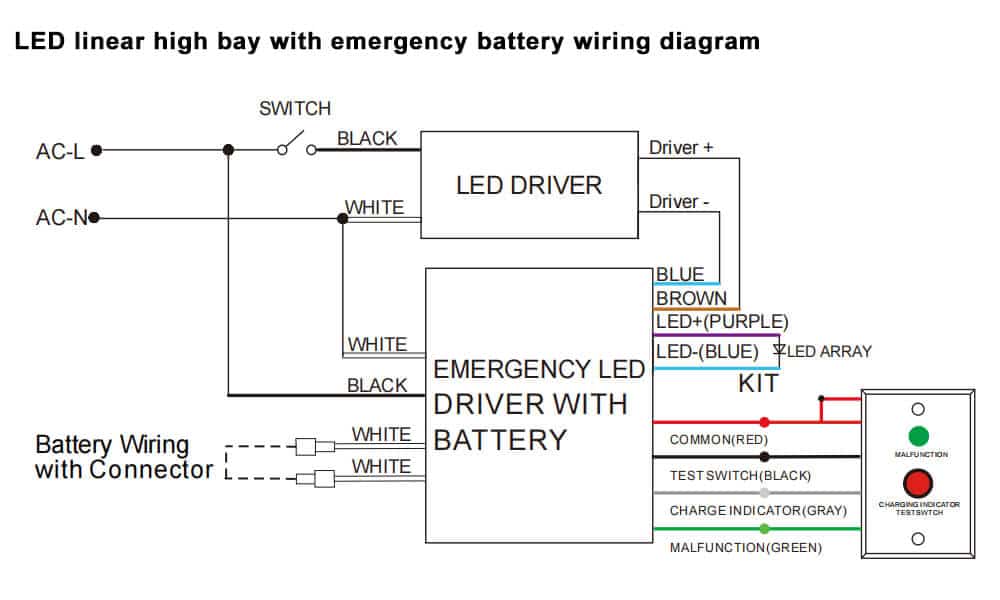
“Home solar plus battery backup wiring for emergencies”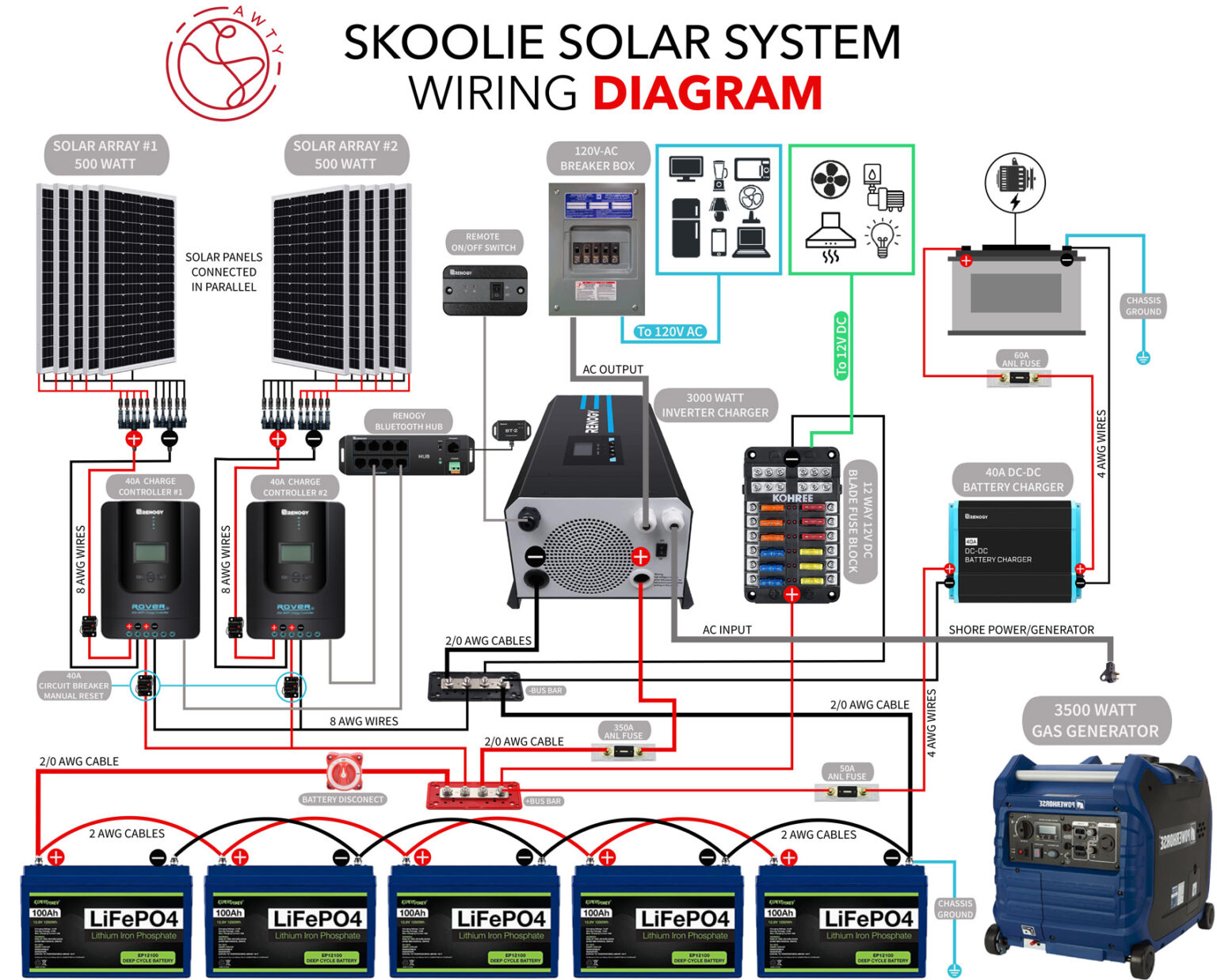
However, with the growing demand for uninterrupted power supply, homeowners are now looking for ways to ensure their solar systems can provide backup power during emergencies. One way to achieve this is by integrating a battery backup system with their existing solar panel setup. In this article, we will delve into the world of home solar plus battery backup wiring for emergencies, exploring the benefits, components, and wiring requirements for a seamless and efficient system.
Introduction to Home Solar Systems
Before we dive into the details of battery backup wiring, let’s take a brief look at how home solar systems work. A typical home solar system consists of solar panels, a mounting system, an inverter, and a grid tie system. The solar panels convert sunlight into DC (direct current) electricity, which is then fed into an inverter that converts the DC power into AC (alternating current) electricity. The AC power is then synchronized with the grid, allowing homeowners to use the electricity generated by their solar panels or sell any excess energy back to the utility company.
The Need for Battery Backup
While home solar systems can provide significant savings on energy bills, they are not always reliable during emergencies. During power outages, solar panels alone cannot provide backup power, as they require a functioning grid connection to operate. This is where battery backup systems come into play. By integrating a battery backup system with their solar panel setup, homeowners can ensure a steady supply of power during emergencies, such as grid failures, natural disasters, or maintenance outages.
Components of a Home Solar Plus Battery Backup System
A home solar plus battery backup system consists of several key components:
- Solar Panels: These are the same solar panels used in a traditional home solar system.
- Inverter/Charger: This device not only converts DC power from the solar panels to AC power but also charges the battery backup system.
- Battery Bank: This is the heart of the backup system, consisting of deep cycle batteries that store excess energy generated by the solar panels.
- Charge Controller: This device regulates the flow of energy between the solar panels, battery bank, and inverter/charger.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): This device automatically switches between the grid and battery backup systems during power outages.

Wiring Requirements for a Home Solar Plus Battery Backup System
To ensure a safe and efficient home solar plus battery backup system, proper wiring is crucial. Here are some key wiring requirements to consider:

- DC Wiring: DC wiring connects the solar panels to the charge controller and inverter/charger. This wiring must be sized correctly to handle the maximum DC current output of the solar panels.
- AC Wiring: AC wiring connects the inverter/charger to the ATS and the grid. This wiring must be sized correctly to handle the maximum AC power output of the inverter/charger.
- Battery Wiring: Battery wiring connects the battery bank to the inverter/charger and charge controller. This wiring must be sized correctly to handle the maximum DC current output of the battery bank.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding are critical to ensure the safe operation of the system. The grounding system must be connected to the battery bank, inverter/charger, and solar panels.
- Overcurrent Protection: Overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, must be installed to protect the wiring and components from overcurrent conditions.
/GettyImages-1270012506-3d1791e86fee42498c8bb4cdd9c3bff4.jpg)
Design Considerations for a Home Solar Plus Battery Backup System
When designing a home solar plus battery backup system, several factors must be considered to ensure the system meets the homeowner’s energy needs and provides reliable backup power during emergencies. Some key design considerations include:
- Load Calculation: Calculate the total load that the backup system needs to support, including critical loads such as lighting, refrigeration, and communication systems.
- Battery Bank Sizing: Size the battery bank to provide the required backup power for the calculated load.
- Inverter/Charger Sizing: Size the inverter/charger to handle the maximum AC power output required by the load.
- Solar Panel Sizing: Size the solar panel array to provide the required energy to charge the battery bank and support the load.
- System Monitoring: Install a system monitoring device to track the performance of the system, including energy production, energy storage, and energy consumption.
Installation and Testing of a Home Solar Plus Battery Backup System
Once the system has been designed and the components have been selected, the installation process can begin. Here are some key installation and testing steps:
- Install the Solar Panel Array: Install the solar panel array, ensuring proper alignment and mounting.
- Install the Inverter/Charger: Install the inverter/charger, connecting it to the solar panel array and battery bank.
- Install the Battery Bank: Install the battery bank, connecting it to the inverter/charger and charge controller.
- Install the ATS: Install the ATS, connecting it to the inverter/charger and grid.
- Test the System: Test the system to ensure it is functioning correctly, including the transfer switch, inverter/charger, and battery bank.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of a Home Solar Plus Battery Backup System
To ensure the system continues to operate efficiently and provide reliable backup power, regular maintenance is crucial. Here are some key maintenance and troubleshooting steps:
- Monitor the System: Regularly monitor the system to track performance and identify any issues.
- Clean the Solar Panels: Clean the solar panels regularly to ensure optimal energy production.
- Check the Battery Bank: Check the battery bank regularly to ensure it is functioning correctly and providing the required backup power.
- Check the Inverter/Charger: Check the inverter/charger regularly to ensure it is functioning correctly and providing the required AC power.
- Troubleshoot Issues: Troubleshoot any issues that arise, including faulty components, wiring issues, or system malfunctions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a home solar plus battery backup system can provide a reliable and efficient source of backup power during emergencies. By understanding the components, wiring requirements, design considerations, installation and testing procedures, and maintenance and troubleshooting steps, homeowners can ensure their system provides the required backup power and energy savings. As the demand for renewable energy sources continues to grow, home solar plus battery backup systems will become increasingly popular, providing a reliable and sustainable source of energy for homes and businesses.