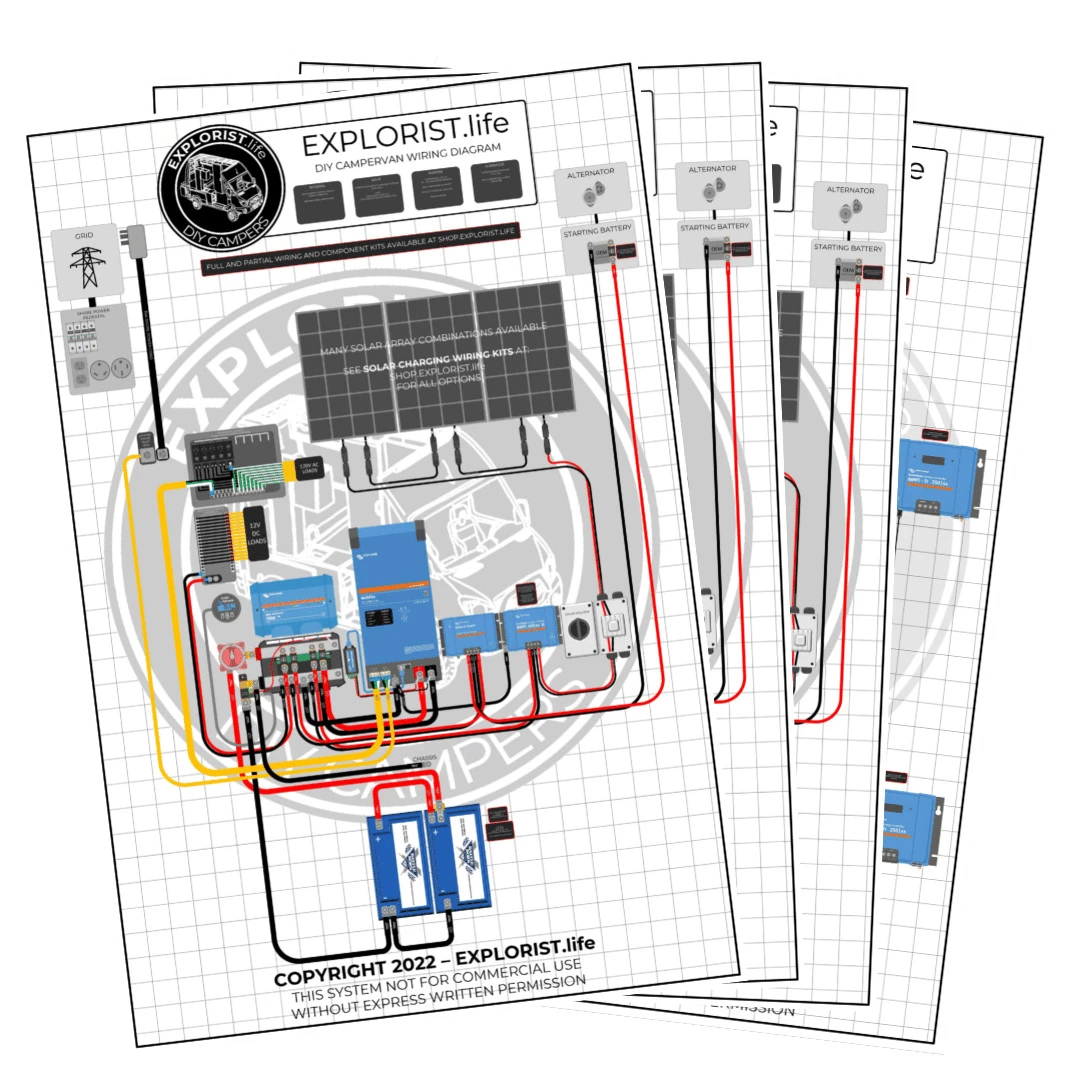
House Solar Power System Wiring Diagram
“House solar power system wiring diagram”
A well-designed solar power system can significantly reduce your electricity bills and carbon footprint. However, installing a solar power system requires careful planning and attention to detail, particularly when it comes to the wiring diagram. In this article, we will delve into the world of house solar power system wiring diagrams, exploring the key components, design considerations, and best practices for a safe and efficient installation.
Introduction to Solar Power Systems
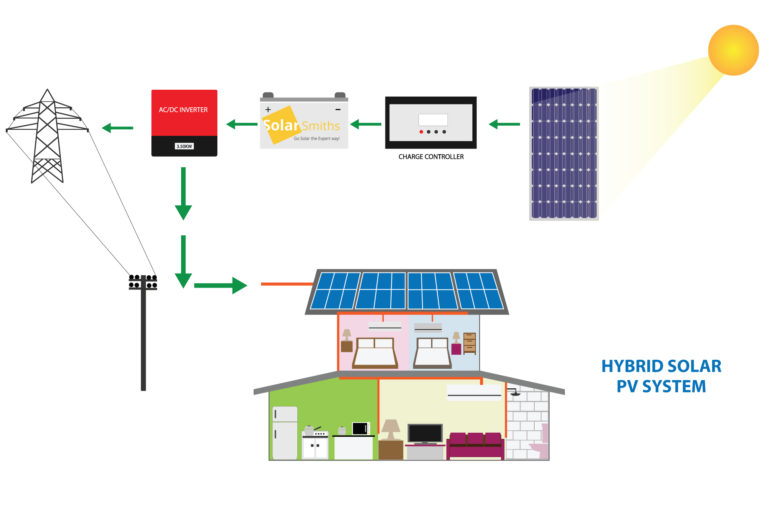
A solar power system, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) system, converts sunlight into electrical energy using solar panels. The system consists of several components, including:
- Solar Panels: These are the photovoltaic modules that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Mounting System: This includes the racks, clamps, and other hardware that secure the solar panels to the roof or ground.
- Inverter: This device converts the DC electricity from the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is usable in the home.
- Charge Controller: This component regulates the flow of energy from the solar panels to the battery bank, if present.
- Battery Bank: This stores excess energy generated by the solar panels for use during periods of low sunlight or at night.
- Electrical Panel: This is the main distribution panel for the home’s electrical system, where the solar power system is connected.

House Solar Power System Wiring Diagram
A wiring diagram is a visual representation of the electrical connections between the various components of the solar power system. A well-designed wiring diagram is essential for a safe and efficient installation. The following are the key components of a house solar power system wiring diagram:
- Solar Panel Array: The solar panel array is the collection of solar panels connected in series and/or parallel to form a single electrical circuit.
- Inverter Input: The inverter input circuit connects the solar panel array to the inverter.
- Inverter Output: The inverter output circuit connects the inverter to the electrical panel.
- Charge Controller: The charge controller circuit connects the solar panel array to the battery bank, if present.
- Battery Bank: The battery bank circuit connects the battery bank to the inverter and the electrical panel.
- Grounding System: The grounding system connects the solar power system to the earth, providing a safe path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault.

Design Considerations
When designing a house solar power system wiring diagram, several factors must be considered to ensure a safe and efficient installation:
- Voltage and Current: The voltage and current ratings of the solar panels, inverter, and other components must be compatible to ensure efficient energy transfer.
- Wiring Size and Type: The wiring size and type must be sufficient to handle the maximum current and voltage of the system.
- Overcurrent Protection: Overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, must be installed to protect the system from excessive current flow.
- Grounding and Bonding: The grounding and bonding system must be designed to provide a safe path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault.
- Monitoring and Control: The system must include monitoring and control devices, such as meters and disconnects, to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Best Practices for Installation
To ensure a safe and efficient installation, the following best practices should be followed:
- Hire a Qualified Installer: A qualified installer with experience in solar power system installations should be hired to design and install the system.
- Follow Local Electrical Codes: The installation must comply with local electrical codes and regulations.
- Use High-Quality Components: High-quality components, such as solar panels and inverters, should be used to ensure efficient energy transfer and long system lifespan.
- Test and Inspect the System: The system must be thoroughly tested and inspected before commissioning to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Provide Ongoing Maintenance: Ongoing maintenance, such as cleaning the solar panels and checking the system’s performance, must be provided to ensure optimal system performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When designing and installing a house solar power system wiring diagram, several common mistakes should be avoided:
- Inadequate Wiring Size: Using wiring that is too small can lead to overheating, fires, and system failure.
- Inadequate Overcurrent Protection: Failing to install overcurrent protection devices can lead to excessive current flow, causing damage to the system and potentially resulting in a fire.
- Poor Grounding and Bonding: A poorly designed grounding and bonding system can lead to electrical shock and system failure.
- Incompatible Components: Using components that are not compatible can lead to inefficient energy transfer and system failure.
- Lack of Monitoring and Control: Failing to install monitoring and control devices can lead to system failures and reduced performance.
Conclusion
A house solar power system wiring diagram is a critical component of a solar power system installation. A well-designed wiring diagram ensures safe and efficient energy transfer, while a poorly designed diagram can lead to system failures, fires, and electrical shock. By following the design considerations, best practices, and avoiding common mistakes outlined in this article, homeowners and installers can ensure a safe and efficient solar power system installation. As the world continues to shift towards renewable energy sources, the importance of a well-designed solar power system wiring diagram cannot be overstated.