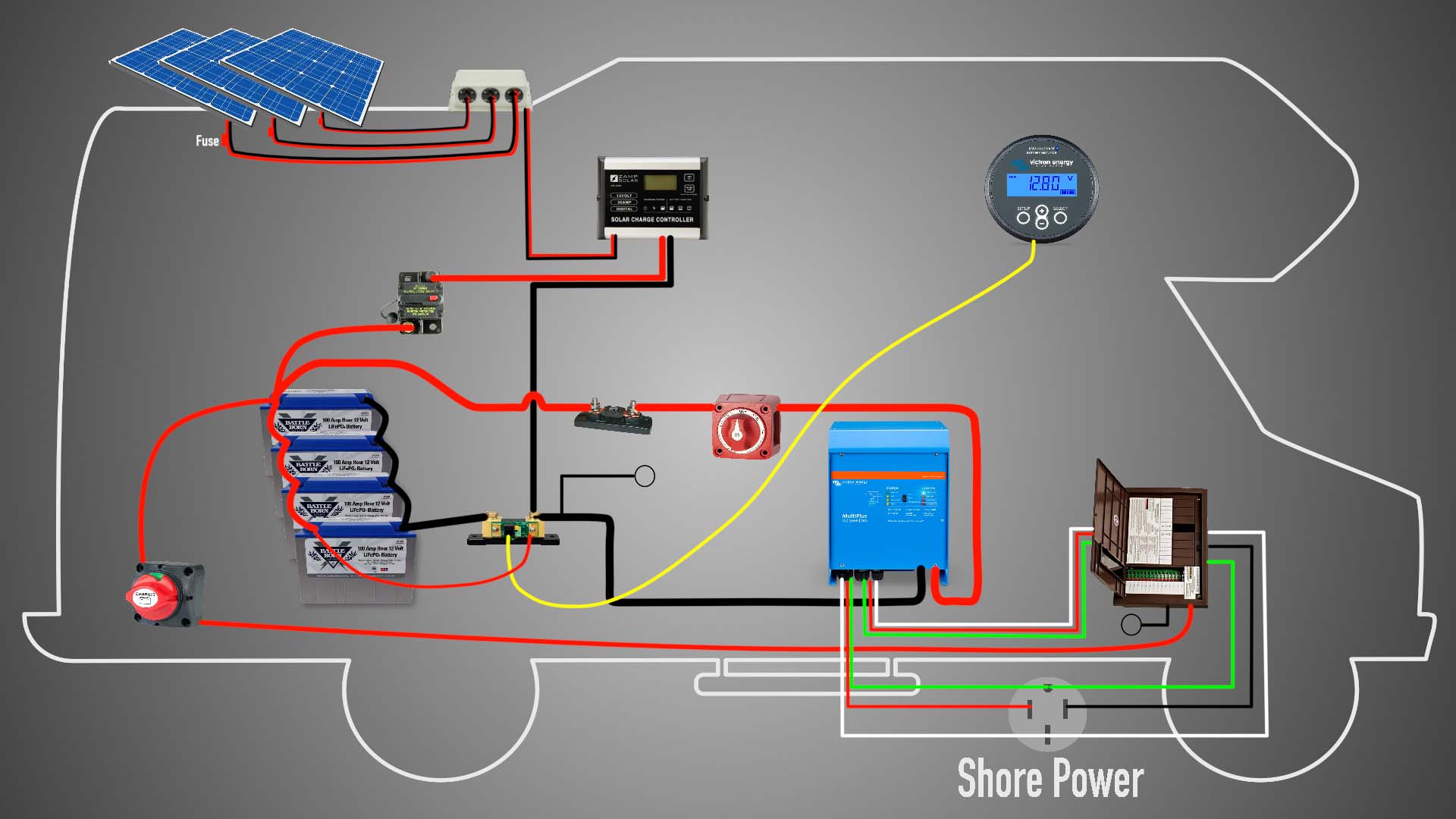
Solar Power Wiring Plans For Residential Homes
“Solar power wiring plans for residential homes”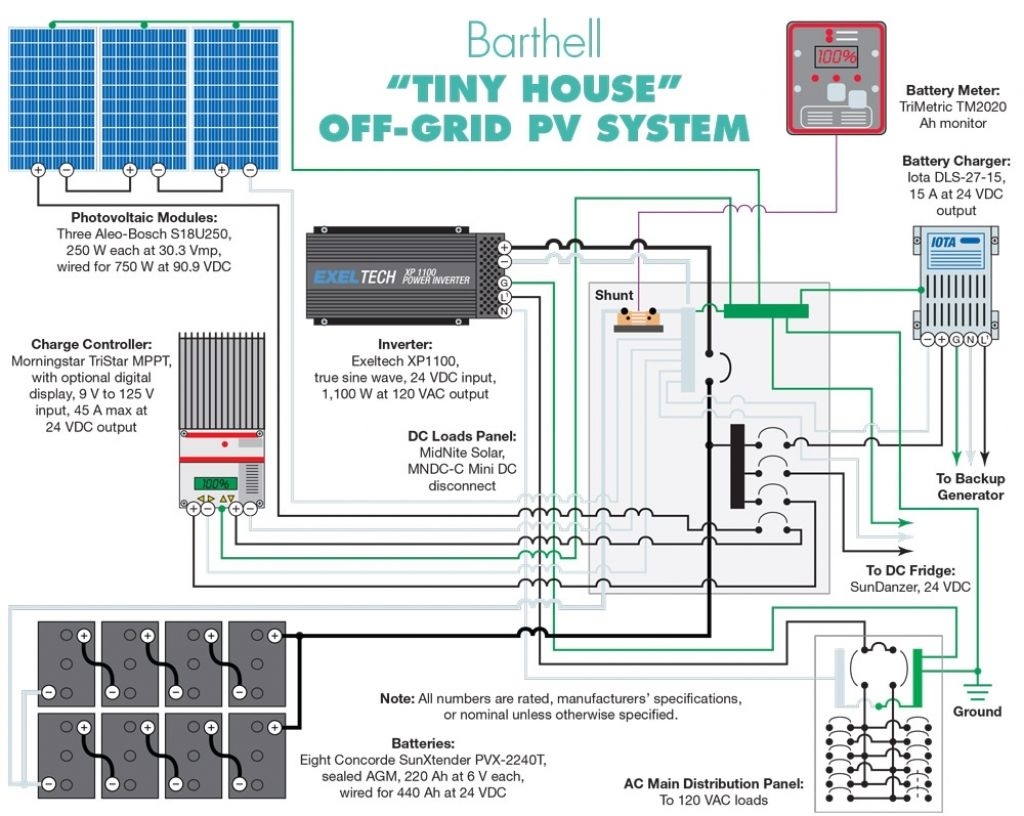
Not only does it reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, but it also helps to decrease energy costs and carbon emissions. However, installing a solar power system requires careful planning and consideration, particularly when it comes to wiring. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to solar power wiring plans for residential homes, covering the essential components, safety considerations, and best practices.
Introduction to Solar Power Systems
A solar power system consists of several key components, including:
- Solar Panels: These are the photovoltaic (PV) panels that convert sunlight into electrical energy.
- Mounting System: This is the framework that supports the solar panels and ensures they are securely attached to the roof or ground.
- Inverter: This device converts the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power, which can be used in the home.
- Charge Controller: This component regulates the flow of energy from the solar panels to the battery bank, if present.
- Battery Bank: This is an optional component that stores excess energy generated by the solar panels for later use.
- Wiring and Electrical Connections: These are the conduits and connectors that link the various components of the solar power system together.

Solar Power Wiring Plans
A well-designed solar power wiring plan is essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the system. The following are some key considerations:
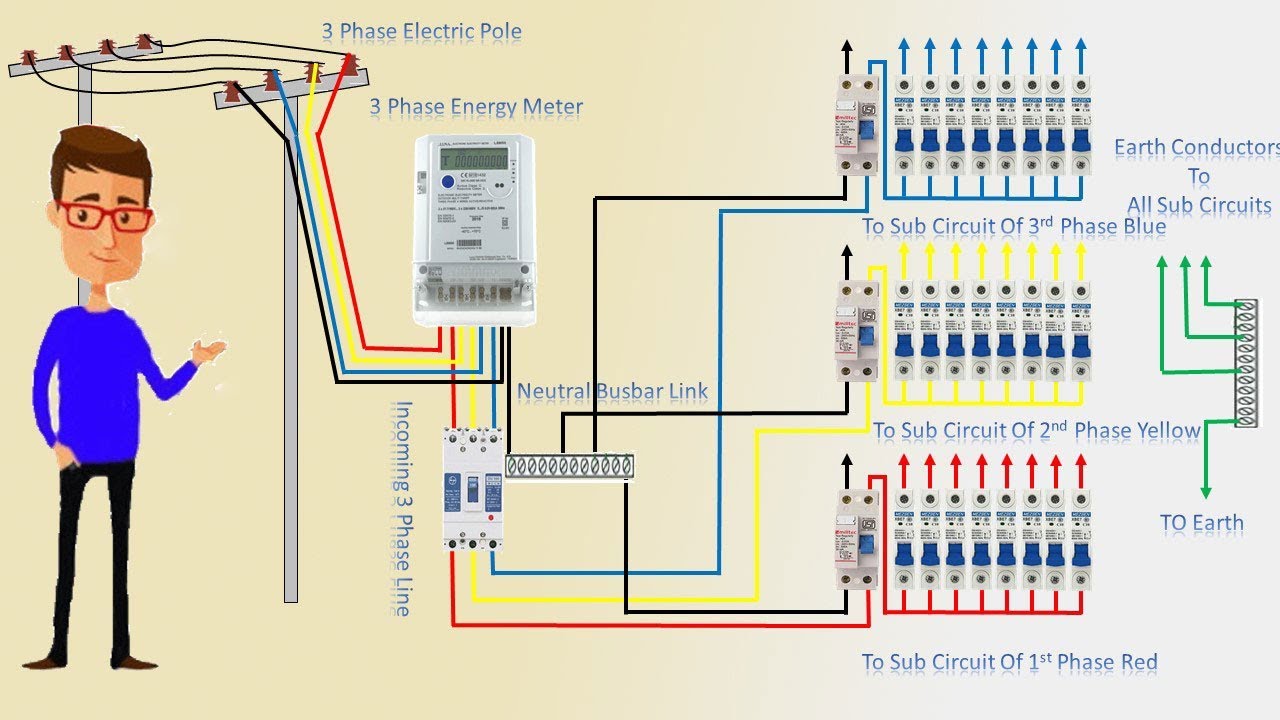
- System Voltage: The voltage of the solar power system will depend on the type and number of solar panels used. Typical system voltages range from 12V to 600V.
- Wiring Size and Type: The size and type of wiring used will depend on the system voltage and current. Thicker wires are required for higher voltage and current systems.
- Conduit and Connectors: The conduit and connectors used to link the components of the solar power system must be rated for the system voltage and current.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding of the solar power system are critical to ensure safety and prevent electrical shock.
- Overcurrent Protection: Overcurrent protection devices, such as fuses or circuit breakers, must be installed to protect the system from excessive current.
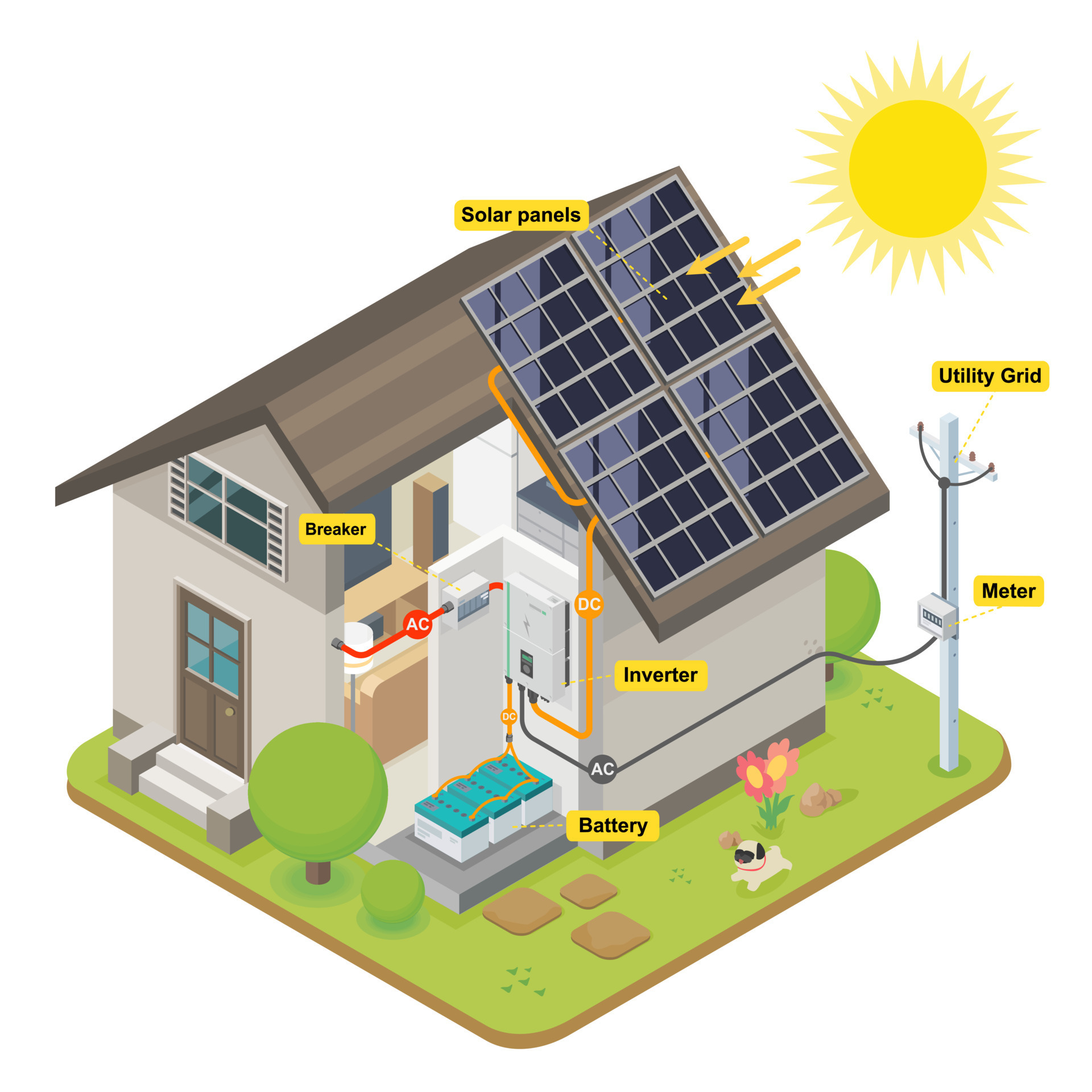
Safety Considerations
Safety is a top priority when designing and installing a solar power system. The following are some key safety considerations:
- Electrical Shock: Electrical shock can occur if the system is not properly grounded or if there is a fault in the wiring.
- Fire Risk: Fire can occur if the system is not properly installed or maintained, or if there is a fault in the wiring or components.
- Arc Faults: Arc faults can occur if there is a loose connection or a fault in the wiring, which can cause a fire or electrical shock.
Best Practices for Solar Power Wiring
To ensure a safe and efficient solar power system, the following best practices should be followed:
- Hire a Licensed Electrician: A licensed electrician should be hired to design and install the solar power system.
- Use High-Quality Components: High-quality components, including wiring, conduit, and connectors, should be used to ensure the system operates safely and efficiently.
- Follow Local Electrical Codes: Local electrical codes and regulations should be followed to ensure the system is installed and operates safely.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including inspections and testing, should be performed to ensure the system operates safely and efficiently.
Solar Power Wiring Plans for Residential Homes
The following are some common solar power wiring plans for residential homes:
- Grid-Tie System: A grid-tie system is the most common type of solar power system, where the solar panels are connected to the grid and excess energy is sold back to the utility company.
- Off-Grid System: An off-grid system is used in areas where there is no access to the grid, and the solar panels are used to charge a battery bank, which provides power to the home.
- Hybrid System: A hybrid system combines a grid-tie system with a battery bank, which provides backup power during outages.
Components of a Residential Solar Power System
The following are the typical components of a residential solar power system:
- Solar Panels: 10-20 solar panels, each with a power output of 300-400W.
- Inverter: A single-phase inverter with a power output of 5-10kW.
- Mounting System: A roof-mounted or ground-mounted system, depending on the location and type of solar panels.
- Wiring and Electrical Connections: 10-20mm² wiring, depending on the system voltage and current.
- Charge Controller: A charge controller with a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) function, if a battery bank is present.
- Battery Bank: A deep cycle battery bank with a capacity of 10-20kWh, if present.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solar power wiring plans for residential homes require careful consideration and planning to ensure a safe and efficient system. By following the best practices outlined in this article, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of solar power while minimizing the risks associated with electrical shock, fire, and arc faults. It is essential to hire a licensed electrician and use high-quality components to ensure the system operates safely and efficiently. With the right design and installation, a solar power system can provide a reliable and renewable source of energy for residential homes.
Recommendations
- Conduct a Site Assessment: Conduct a site assessment to determine the suitability of the location for a solar power system.
- Choose a Reputable Installer: Choose a reputable installer with experience in designing and installing solar power systems.
- Use High-Quality Components: Use high-quality components, including wiring, conduit, and connectors, to ensure the system operates safely and efficiently.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including inspections and testing, should be performed to ensure the system operates safely and efficiently.
- Monitor System Performance: Monitor system performance to optimize energy production and identify any issues that may arise.
By following these recommendations and best practices, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of solar power while minimizing the risks associated with electrical shock, fire, and arc faults. As the world continues to shift towards renewable energy sources, solar power will play an increasingly important role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing carbon emissions.