Grid-tied Solar Inverter Wiring Diagram
“Grid-tied solar inverter wiring diagram”
One of the most crucial components of a solar power system is the grid-tied solar inverter, which converts the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that can be fed into the grid. In this article, we will delve into the world of grid-tied solar inverter wiring diagrams, exploring the intricacies of these systems and providing a comprehensive guide for installers, electricians, and DIY enthusiasts.
Introduction to Grid-tied Solar Inverters
A grid-tied solar inverter is a device that connects a solar panel array to the utility grid, allowing homeowners and businesses to sell excess energy back to the grid and offset their energy bills. These inverters are designed to synchronize with the grid’s frequency and voltage, ensuring a seamless transition between solar-generated power and grid power.
Components of a Grid-tied Solar Inverter System
A typical grid-tied solar inverter system consists of the following components:
- Solar Panels: These are the photovoltaic (PV) panels that generate DC power from sunlight.
- Mounting Structure: This is the framework that supports the solar panels and tilts them at an optimal angle to maximize energy production.
- Inverter: This is the device that converts the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power that can be fed into the grid.
- AC Panel: This is the electrical panel that distributes the AC power generated by the inverter to the load center or main electrical panel.
- Load Center: This is the main electrical panel that distributes power to the various circuits in the building.
- Utility Meter: This is the meter that measures the amount of energy consumed by the building and the amount of excess energy generated by the solar panel array.
- Grounding System: This is the system that grounds the solar panel array and inverter to prevent electrical shock and ensure safe operation.

Wiring Diagram for a Grid-tied Solar Inverter System
A typical wiring diagram for a grid-tied solar inverter system is shown below:
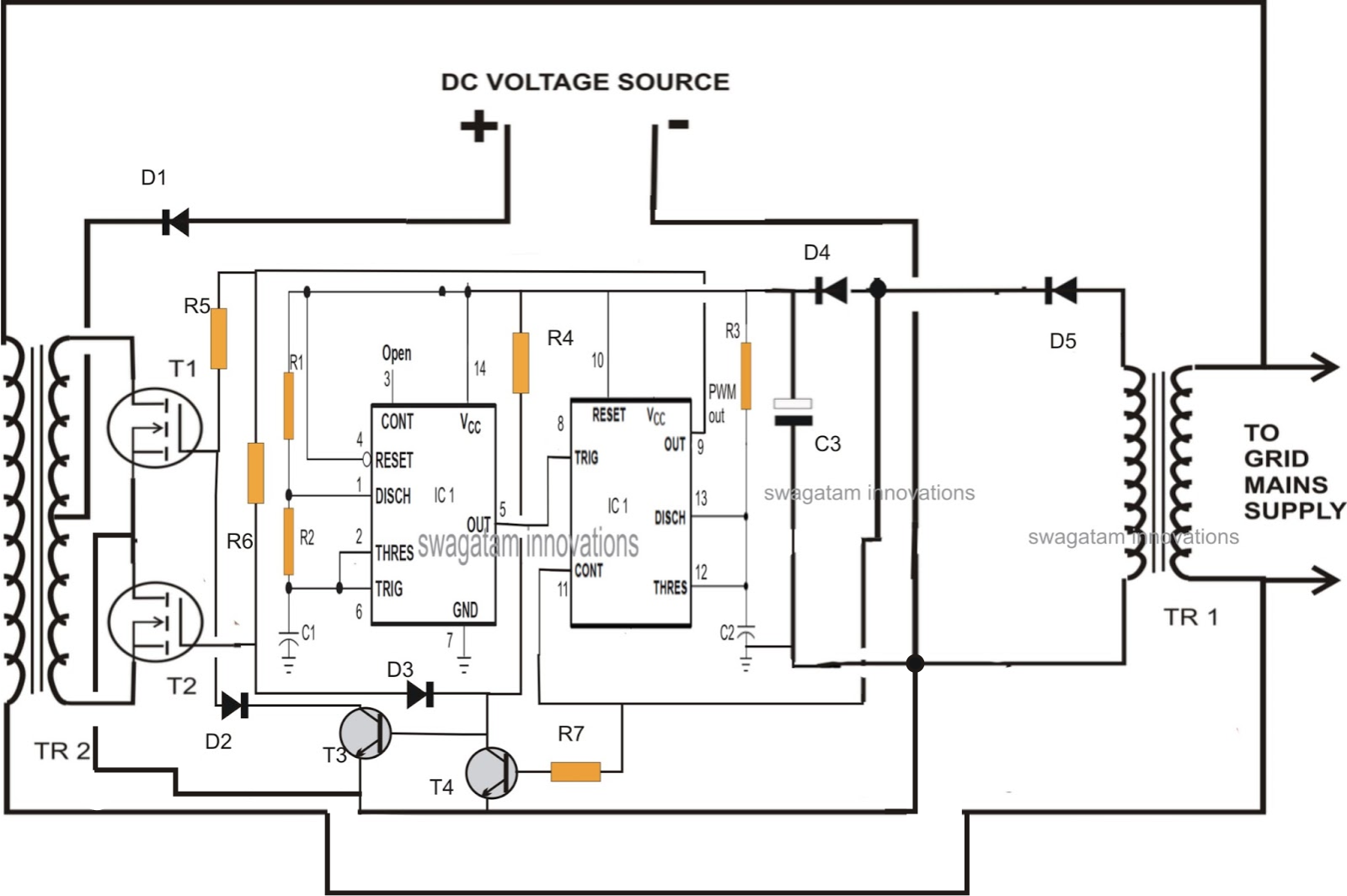
[Insert diagram]
The diagram illustrates the following connections:
- Solar Panel Array: The solar panel array is connected to the inverter using DC wiring.
- Inverter: The inverter is connected to the AC panel using AC wiring.
- AC Panel: The AC panel is connected to the load center using AC wiring.
- Load Center: The load center is connected to the utility meter using AC wiring.
- Utility Meter: The utility meter is connected to the grid using AC wiring.
- Grounding System: The grounding system is connected to the solar panel array, inverter, and AC panel to provide a safe path to ground.
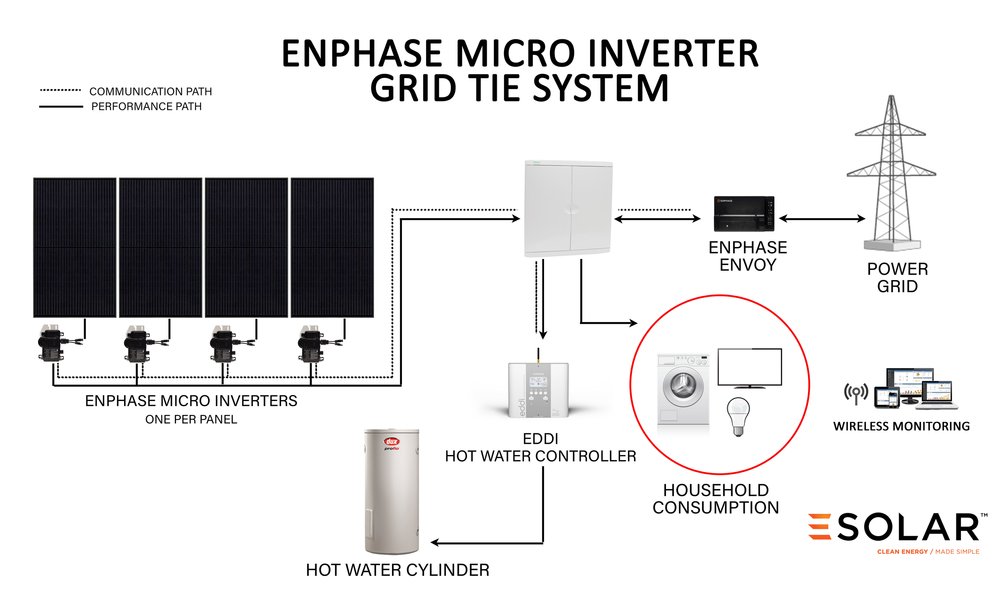
Wiring Requirements for a Grid-tied Solar Inverter System
When wiring a grid-tied solar inverter system, it is essential to follow the relevant electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electric Code (NEC) in the United States. Some of the key wiring requirements include:
- Wire Size: The wire size must be sufficient to carry the maximum current generated by the solar panel array.
- Insulation: The wiring must be insulated to prevent electrical shock and ensure safe operation.
- Color Coding: The wiring must be color-coded to identify the different phases and neutrals.
- Grounding: The wiring must be grounded to prevent electrical shock and ensure safe operation.
- Disconnects: Disconnects must be installed to allow for safe maintenance and repair of the system.
Installation Considerations for a Grid-tied Solar Inverter System
When installing a grid-tied solar inverter system, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- System Sizing: The system must be sized to meet the energy needs of the building.
- Panel Orientation: The solar panels must be oriented to maximize energy production.
- Shading: The solar panels must be installed to minimize shading, which can reduce energy production.
- Ventilation: The inverter and other electrical components must be installed in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Grounding: The system must be grounded to prevent electrical shock and ensure safe operation.
Maintenance and Repair of a Grid-tied Solar Inverter System
Regular maintenance and repair are essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of a grid-tied solar inverter system. Some of the key maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning: The solar panels must be cleaned regularly to ensure maximum energy production.
- Inspection: The system must be inspected regularly to identify any potential issues or faults.
- Replacement: Components must be replaced as needed to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Software Updates: The inverter software must be updated regularly to ensure compatibility with the grid and to optimize energy production.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a grid-tied solar inverter wiring diagram is a critical component of a solar power system, connecting the solar panel array to the utility grid and allowing homeowners and businesses to sell excess energy back to the grid. By following the relevant electrical codes and standards, and considering the key installation, maintenance, and repair factors, installers, electricians, and DIY enthusiasts can ensure the safe and efficient operation of a grid-tied solar inverter system. As the world continues to shift towards renewable energy sources, the importance of grid-tied solar inverter systems will only continue to grow, making them an essential component of our energy future.
Additional Resources
For those interested in learning more about grid-tied solar inverter systems, the following resources are recommended:
- National Electric Code (NEC): The NEC provides guidelines for the safe installation of electrical systems, including grid-tied solar inverter systems.
- International Association of Electrical Inspectors (IAEI): The IAEI provides training and resources for electrical inspectors and installers, including information on grid-tied solar inverter systems.
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA): The SEIA provides information and resources on solar energy, including grid-tied solar inverter systems.
- Inverter Manufacturer Documentation: Inverter manufacturers provide documentation and resources on the installation, maintenance, and repair of their products.
By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, and consulting the recommended resources, installers, electricians, and DIY enthusiasts can ensure the safe and efficient operation of a grid-tied solar inverter system, and contribute to a sustainable energy future.
