Standalone Solar Panel Wiring For Residential Use
“Standalone solar panel wiring for residential use”
Standalone solar panel systems, in particular, offer a reliable and efficient way to harness the sun’s energy and reduce reliance on the grid. However, wiring these systems can be complex and requires careful planning to ensure safety and optimal performance. In this article, we will delve into the world of standalone solar panel wiring for residential use, exploring the key components, wiring configurations, and best practices for a successful installation.
Introduction to Standalone Solar Panel Systems
A standalone solar panel system, also known as an off-grid system, is a self-sufficient energy generation unit that operates independently of the grid. These systems typically consist of solar panels, a charge controller, a battery bank, and an inverter. The solar panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then stored in the battery bank via the charge controller. The inverter converts the stored DC power into alternating current (AC) electricity, suitable for residential use.
Key Components of a Standalone Solar Panel System
Before diving into the wiring aspect, it’s essential to understand the key components of a standalone solar panel system:
- Solar Panels: These are the primary energy generators of the system, converting sunlight into DC electricity.
- Charge Controller: This device regulates the flow of energy from the solar panels to the battery bank, preventing overcharging and ensuring optimal battery performance.
- Battery Bank: A collection of deep cycle batteries that store excess energy generated by the solar panels for later use.
- Inverter: This device converts the stored DC power from the battery bank into AC electricity, suitable for residential use.
- Mounting Hardware: Stands, clamps, and brackets used to secure the solar panels and other system components.
- Wiring and Connectors: The electrical connections between the system components, including cables, connectors, and fuses.

Wiring Configurations for Standalone Solar Panel Systems
The wiring configuration of a standalone solar panel system is critical to its safety and performance. The following are common wiring configurations:
- Series Wiring: Solar panels are connected in series to increase the voltage of the system. This configuration is suitable for smaller systems with fewer panels.
- Parallel Wiring: Solar panels are connected in parallel to increase the current of the system. This configuration is suitable for larger systems with more panels.
- Series-Parallel Wiring: A combination of series and parallel wiring, offering a balance between voltage and current.
Wiring Considerations for Safety and Performance
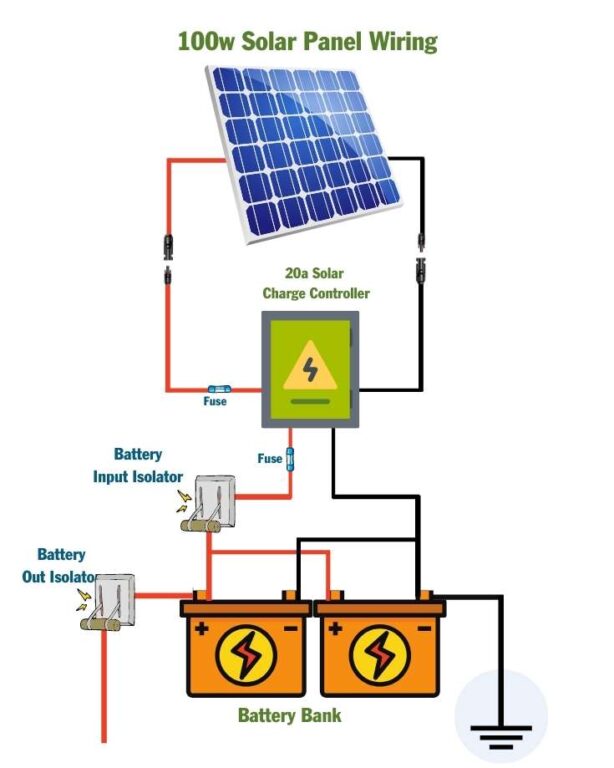
When wiring a standalone solar panel system, it’s essential to consider the following safety and performance factors:
- Voltage Drop: Ensure that the wiring configuration minimizes voltage drop, which can reduce system performance and efficiency.
- Current Rating: Verify that the wiring and connectors can handle the maximum current output of the system.
- Short Circuit Protection: Install fuses or circuit breakers to protect the system from short circuits and overloads.
- Grounding: Ensure that the system is properly grounded to prevent electrical shock and equipment damage.
- Insulation and Protection: Use insulation and protection materials to prevent wiring damage from environmental factors, such as UV radiation, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Best Practices for Standalone Solar Panel Wiring
To ensure a safe and efficient standalone solar panel wiring system, follow these best practices:
- Hire a Qualified Electrician: Engage a qualified electrician with experience in solar panel installations to design and wire the system.
- Use High-Quality Materials: Select wiring, connectors, and other system components that meet or exceed industry standards for safety and performance.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for each system component, including wiring and installation guidelines.
- Conduct Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the system to prevent equipment failure and ensure optimal performance.
- Monitor System Performance: Install monitoring equipment to track system performance, identify issues, and optimize energy production.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Standalone Solar Panel Wiring
When wiring a standalone solar panel system, avoid the following common mistakes:
- Inadequate Wire Sizing: Using wire that is too small for the system, leading to voltage drop and reduced performance.
- Insufficient Grounding: Failing to properly ground the system, increasing the risk of electrical shock and equipment damage.
- Incorrect Wiring Configuration: Using an incorrect wiring configuration, such as series wiring for a large system, which can reduce performance and efficiency.
- Poor Wire Management: Failing to properly manage wires, increasing the risk of damage, wear, and tear.
- Lack of Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance, leading to equipment failure and reduced system performance.
Conclusion
Standalone solar panel wiring for residential use requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a thorough understanding of the key components and wiring configurations. By following best practices, avoiding common mistakes, and engaging qualified professionals, homeowners can enjoy a safe, efficient, and reliable solar panel system that reduces their reliance on the grid and lowers their energy costs. As the world continues to transition towards renewable energy sources, standalone solar panel systems will play an increasingly important role in shaping a sustainable energy future.
Recommendations for Future Installations
As the solar industry continues to evolve, it’s essential to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies, regulations, and best practices. For future standalone solar panel installations, consider the following recommendations:
- Monitor Advancements in Technology: Stay informed about new technologies, such as energy storage systems and smart inverters, which can enhance system performance and efficiency.
- Comply with Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local and national regulations, such as building codes and electrical standards, to ensure compliance and safety.
- Invest in Energy Storage: Consider investing in energy storage systems, such as batteries, to optimize energy production and reduce reliance on the grid.
- Optimize System Design: Work with experienced professionals to design a system that meets your energy needs and budget, taking into account factors such as roof size, shading, and local climate conditions.
- Prioritize Maintenance and Monitoring: Regularly inspect and maintain your system to prevent equipment failure and ensure optimal performance, and invest in monitoring equipment to track system performance and identify areas for improvement.
By following these recommendations and staying committed to best practices, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of standalone solar panel systems while contributing to a sustainable energy future.
